Connect to a Git repository
Harness code repository connectors connect your Harness account with your Git platform. Connectors are used to pull code as well as other important files, such as Helm charts, Kubernetes manifests, and Terraform scripts, from your Git repos.
You can add code repo connectors at the account, organization, or project scopes. This topic assumes you're adding connectors at the project scope, but the process is the same for the other scopes.
Permissions
In general, the Git provider user account you use to set up a connector needs the same permissions it would need if you were working from Git.
This means that, if you are using a Harness code repo connector to pull manifests from a repo, then the user account you use in the connector must have read repo (or equivalent) permissions in your Git provider.
For permissions in the Harness Git Experience, go to Source Code Manager Settings.
SSH Key authentication
If your code repo connector uses SSH Key authentication, the SSH Key is stored as a Harness SSH credential secret, and the SSH credential's Username must be git.
Connect to AWS CodeCommit
You can use either an AWS CodeCommit connector or the platform-agnostic Git connector to connect to AWS CodeCommit repos.
Regardless of which connector you choose, the IAM account you use to connect to CodeCommit must have the following policies:
- AWSCodeCommitPowerUser
- DescribeRegions
The DescribeRegions action is required for all AWS connections, regardless of what AWS resource you use with Harness.
For instructions on setting up the IAM user for CodeCommit connections, go to the following AWS documentation:
- AWS CodeCommit connector
- Platform-agnostic Git connector
In your Harness project, select Connectors under Project Setup.
Select New Connector and select AWS CodeCommit under Code Repositories.
Configure the AWS CodeCommit connector settings:
- Enter a Name.
- Select Repository to connect to one repo or select Region to connect to an entire AWS region. Selecting Region lets you use one connector for all repos in that region.
- If you selected Repository, enter the AWS CodeCommit Repository URL, such as
https://git-codecommit.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/v1/repos/doc-text. You can get this URL from your CodeCommit repo by using its Clone URL menu and selecting Clone HTTPS. - If you selected Region, provide the name of a repo that Harness can use to test the connection.
- In Access Key and Secret Key, enter the IAM user's access key and secret key, respectively. Use Encrypted text secrets to store keys.
After the connection test runs, select Finish to save the connector.
You can connect to CodeCommit using the Harness platform-agnostic Git connector, instead of the AWS CodeCommit connector.
With the generic Git connector, you must use a username and password for the IAM user, instead of an access key and secret key.
On the configuration page for the IAM User, select Security credentials, and then generate credentials in HTTPS Git credentials for AWS CodeCommit.
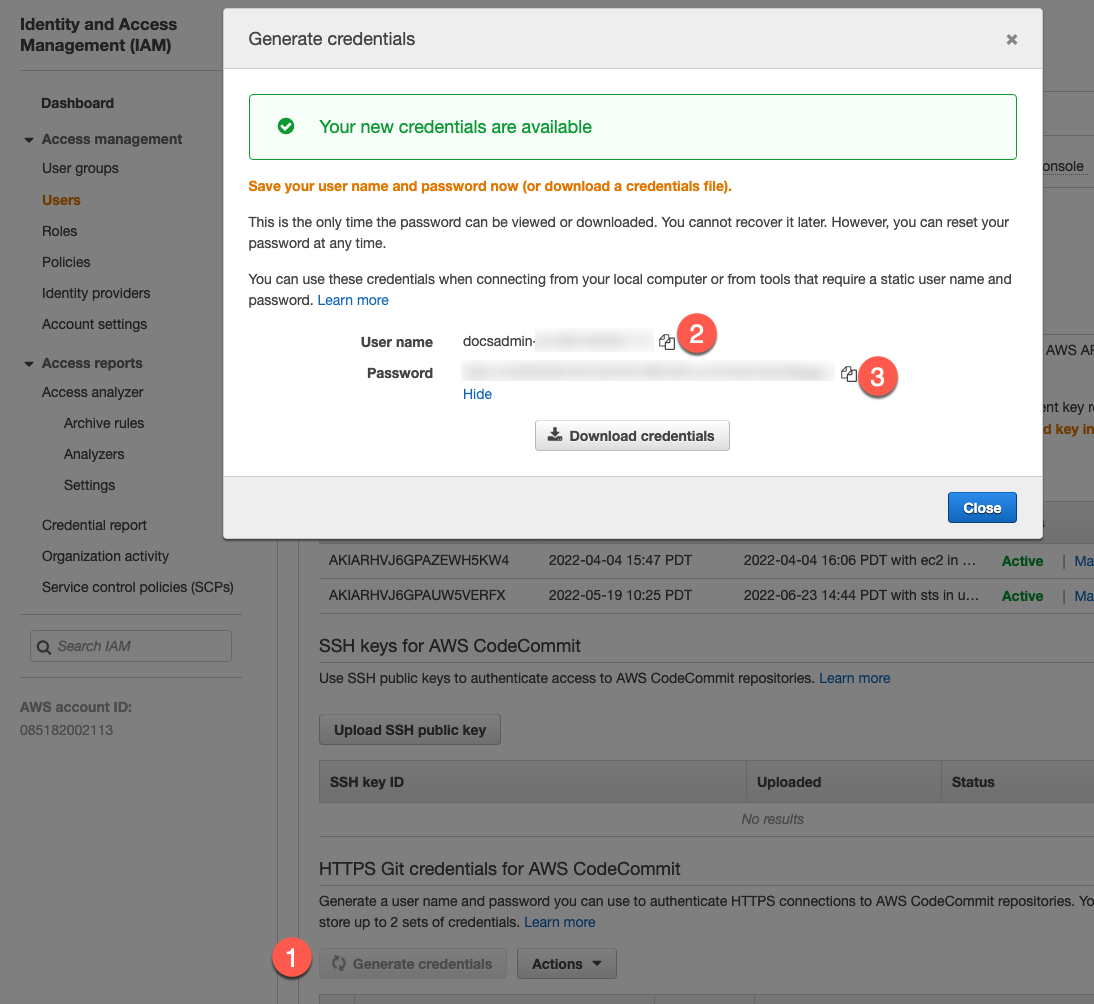
In your Harness project, select Connectors under Project Setup.
Select New Connector and select Git under Code Repositories.
Configure the Git connector settings:
- Enter a Name.
- Select Repository for the URL Type.
- Select HTTP for the Connection Type.
- In Git Repository URL, enter the AWS CodeCommit repository URL, such as
https://git-codecommit.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/v1/repos/doc-text. You can get this URL from your CodeCommit repo by using its Clone URL menu and selecting Clone HTTPS. - In Username and Password, enter the username and password that you generated for the IAM user. Use an Encrypted text secret to store the password.
After the connection test runs, select Finish to save the connector.
Connect to Azure Repos
Azure Repos is a set of version control tools that you can use to manage your code. Azure Repos provide the following kinds of version control:
- Git: Distributed version control
- Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC): Centralized version control
For instructions, go to Connect to Azure Repos.
Connect to Bitbucket
Harness supports both Cloud and Data Center (On-Prem) versions of Bitbucket.
- In your Harness project, select Connectors under Project Setup.
- Select New Connector, and select Bitbucket under Code Repositories.
- Configure the Bitbucket connector settings.
- After the connection test runs, select Finish to save the connector.
Connect to GitHub
- In your Harness project, select Connectors under Project Setup.
- Select New Connector, and select GitHub under Code Repositories.
- Configure the GitHub connector settings.
- After the connection test runs, select Finish to save the connector.
Connect to GitLab
- In your Harness project, select Connectors under Project Setup.
- Select New Connector, and select GitLab under Code Repositories.
- Configure the GitLab connector settings.
- After the connection test runs, select Finish to save the connector.
Use the platform-agnostic Git connector
If Harness doesn't have a dedicated code repo connector for your Git provider, or your configuration prevents you from using the platform-specific code repo connector, you can use the platform-agnostic Git connector.
- In your Harness project, select Connectors under Project Setup.
- Select New Connector, and select Git under Code Repositories.
- Configure the Git connector settings.
- After the connection test runs, select Finish to save the connector.
Network connection times out when fetching large repos
Currently, the fetch optimization feature is behind the feature flag OPTIMIZED_GIT_FETCH_FILES. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
Harness performs a git clone to fetch files. When fetching very large repositories, the network connection can time out. With fetch optimization enabled, Harness uses provider-specific APIs to improve performance when fetching very large repos.
If the OPTIMIZED_GIT_FETCH_FILES feature flag is enabled, and your GitHub organization has SAML enabled, the token must be SAML-authorized to access the organization, even if the repository is public. For more information, go to the GitHub documentation on GitHub authentication with SAML single sign-on.