Set up a GCP VM build infrastructure
This build infrastructure option is only available with Harness CI Team and Enterprise plans.
Currently, this feature is behind the Feature Flag CI_VM_INFRASTRUCTURE. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
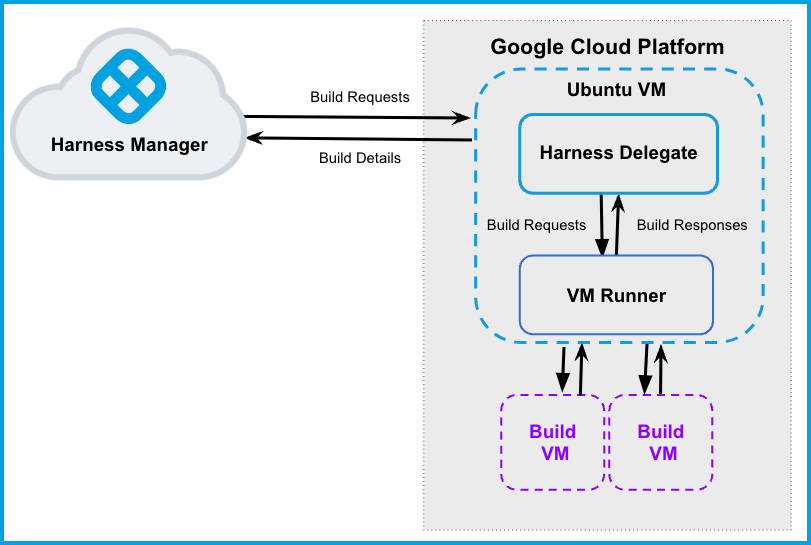
This topic describes how to set up a CI build infrastructure in Google Cloud Platform (GCP). To do this, you will create an Ubuntu VM and then install a Harness Delegate and Drone VM Runner on it. The runner creates VMs dynamically in response to CI build requests.
This is one of several CI build infrastructure options. For example, you can also set up a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure.
The following diagram illustrates a CI build farm. The Harness Delegate communicates directly with your Harness instance. The VM Runner maintains a pool of VMs for running builds. When the delegate receives a build request, it forwards the request to the runner, which runs the build on an available VM.
Prepare the Google Cloud VM
For your Google Cloud VM configuration:
- The delegate VM must use a machine type with 4 vCPU and 16 GB memory or more.
- Harness recommends an Ubuntu 20.04 LTS machine image, such as Focal or Jammy.
- The VM must allow ingress access on ports 22 and 9079.
To find images to use on Google Compute Engine, use gcloud compute images list.
Valid image references follow the format of projects/PROJECT/global/images/IMAGE. For example: projects/docs-test/global/images/ubuntu-pro-1804-bionic-v20220131.
Set up the delegate VM
- Log into the Google Cloud Console and launch the VM that will host your Harness delegate.
- Install Docker on the VM.
- Install Docker Compose on the VM. You must have Docker Compose version 3.7 or higher installed.
- On the VM, run
gcloud auth application-default loginto create anapplication_default_credentials.jsonfile at/home/$(whoami)/.config/gcloud
Configure the Drone pool on the Google VM
The pool.yml file defines the VM spec and pool size for the VM instances used to run the pipeline. A pool is a group of instantiated VMs that are immediately available to run CI pipelines. You can configure multiple pools in pool.yml, such as a Windows VM pool and a Linux VM pool.
Create a
/runnerfolder on your delegate VM andcdinto it:mkdir /runner
cd /runnerIn the
/runnerfolder, create apool.ymlfile.Modify
pool.ymlas described in the following example. For information about specific settings, go to Pool settings reference.
Example pool.yml
version: "1"
instances:
- name: ubuntu-gcp
default: true
type: google
pool: 1
limit: 1
platform:
os: linux
arch: amd64
spec:
account:
project_id: ci-play ## Your Google project ID.
json_path: /path/to/key.json ## Your JSON credentials file.
image: projects/ubuntu-os-pro-cloud/global/images/ubuntu-pro-1804-bionic-v20220510
machine_type: e2-small
zone: ## To minimize latency between delegate and build VMs, specify the same zone where your delegate VM is running.
- us-central1-a
- us-central1-b
- us-central1-c
disk:
size: 100
type: "pd-balanced"
Pool settings reference
You can configure the following settings in your pool.yml file. You can also learn more in the Drone documentation for the Pool File and Google drivers.
| Setting | Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | String | name: windows_pool | Unique identifier of the pool. You will need to specify this pool name in the Harness Manager when you set up the CI stage build infrastructure. |
pool | Integer | pool: 1 | Warm pool size number. Denotes the number of VMs in ready state to be used by the runner. |
limit | Integer | limit: 3 | Maximum number of VMs the runner can create at any time. pool indicates the number of warm VMs, and the runner can create more VMs on demand up to the limit.For example, assume pool: 3 and limit: 10. If the runner gets a request for 5 VMs, it immediately provisions the 3 warm VMs (from pool) and provisions 2 more, which are not warm and take time to initialize. |
platform | Key-value pairs, strings | platform: os: linux arch: amd64 | Specify VM platform operating system (os) and architecture (arch). variant is optional. |
spec | Key-value pairs, various | Go to Example pool.yml. | Configure settings for the build VMs.
|
Start the runner
SSH into the delegate VM and run the following command to start the runner:
$ docker run -v /runner:/runner -p 3000:3000 drone/drone-runner-aws:latest delegate --pool /runner/pool.yml
This command mounts the volume to the Docker container providing access to pool.yml and JSON credentials to authenticate with GCP. It also exposes port 3000 and passes arguments to the container.
Install the delegate
Install a Harness Docker Delegate on your delegate VM.
Create a delegate token. The delegate uses this token to authenticate with the Harness Platform.
- In Harness, go to Account Settings, then Account Resources, and then select Delegates.
- Select Tokens in the header, and then select New Token.
- Enter a token name and select Apply to generate a token.
- Copy the token and store is somewhere you can retrieve it when installing the delegate.
Again, go to Account Settings, then Account Resources, and then Delegates.
Select New Delegate.
Select Docker and enter a name for the delegate.
Copy and run the install command generated in Harness. Make sure the
DELEGATE_TOKENmatches the one you just created.
For more information about delegates and delegate installation, go to Delegate installation overview.
Verify connectivity
Verify that the delegate and runner containers are running correctly. You might need to wait a few minutes for both processes to start. You can run the following commands to check the process status:
$ docker ps
$ docker logs DELEGATE_CONTAINER_ID
$ docker logs RUNNER_CONTAINER_IDIn the Harness UI, verify that the delegate appears in the delegates list. It might take two or three minutes for the Delegates list to update. Make sure the Connectivity Status is Connected. If the Connectivity Status is Not Connected, make sure the Docker host can connect to
https://app.harness.io.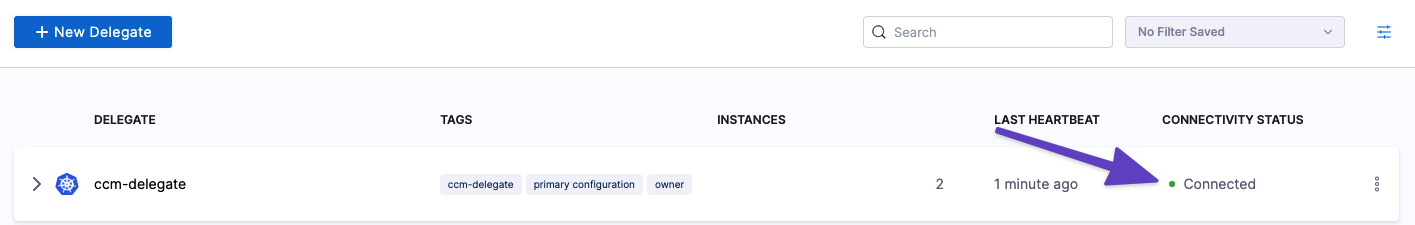
The delegate and runner are now installed, registered, and connected.
Specify build infrastructure
Configure your pipeline's Build (CI) stage to use your GCP VMs as build infrastructure.
- Visual
- YAML
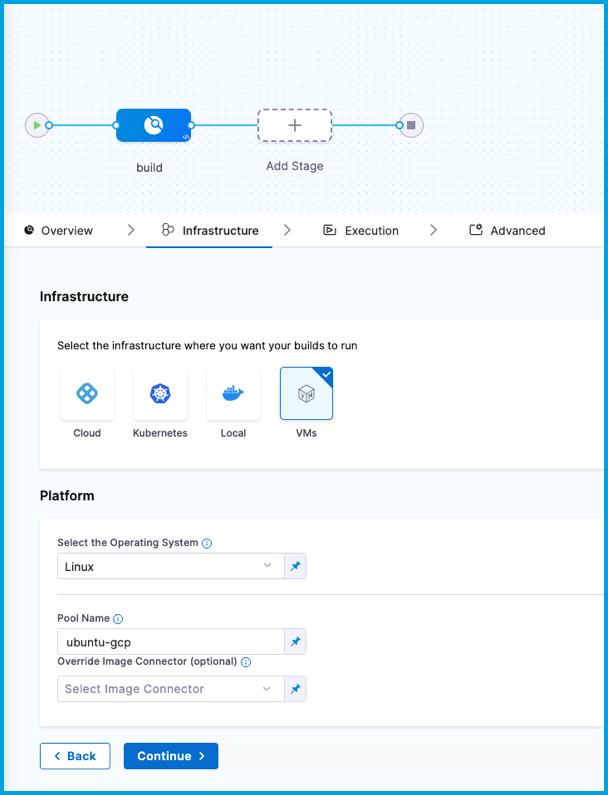
- In Harness, go to the CI pipeline that you want to use the GCP VM build infrastructure.
- Select the Build stage, and then select the Infrastructure tab.
- Select VMs.
- Enter the Pool Name from your pool.yml.
- Save the pipeline.
- stage:
name: build
identifier: build
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
infrastructure:
type: VM
spec:
type: Pool
spec:
poolName: POOL_NAME_FROM_POOL_YML
os: Linux
execution:
steps:
...