Preview with the Terraform Plan step
This topic describes how to run a Terraform script as a Terraform plan using the Harness Terraform Plan step.
You can run the Terraform Plan step to provision any resource, including the target infrastructure for a deployment.
This topic covers using the Terraform Plan step for non-target infrastructure.
For steps on using the Terraform Plan to provision the target infrastructure for a deployment, see Provision Target Deployment Infra Dynamically with Terraform.
Before You Begin
Important: Install Terraform on Delegates
Terraform must be installed on the Delegate to use a Harness Terraform Provisioner. You can install Terraform manually or use the INIT_SCRIPT environment variable in the Delegate YAML.
See Build custom delegate images with third-party tools.
# Install TF
microdnf install unzip
curl -O -L https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/1.3.5/terraform_1.3.5_darwin_amd64.zip
unzip terraform_1.3.5_darwin_amd64.zip
mv ./terraform /usr/bin/
# Check TF install
terraform --version
Review: Terraform Plan and Apply Steps
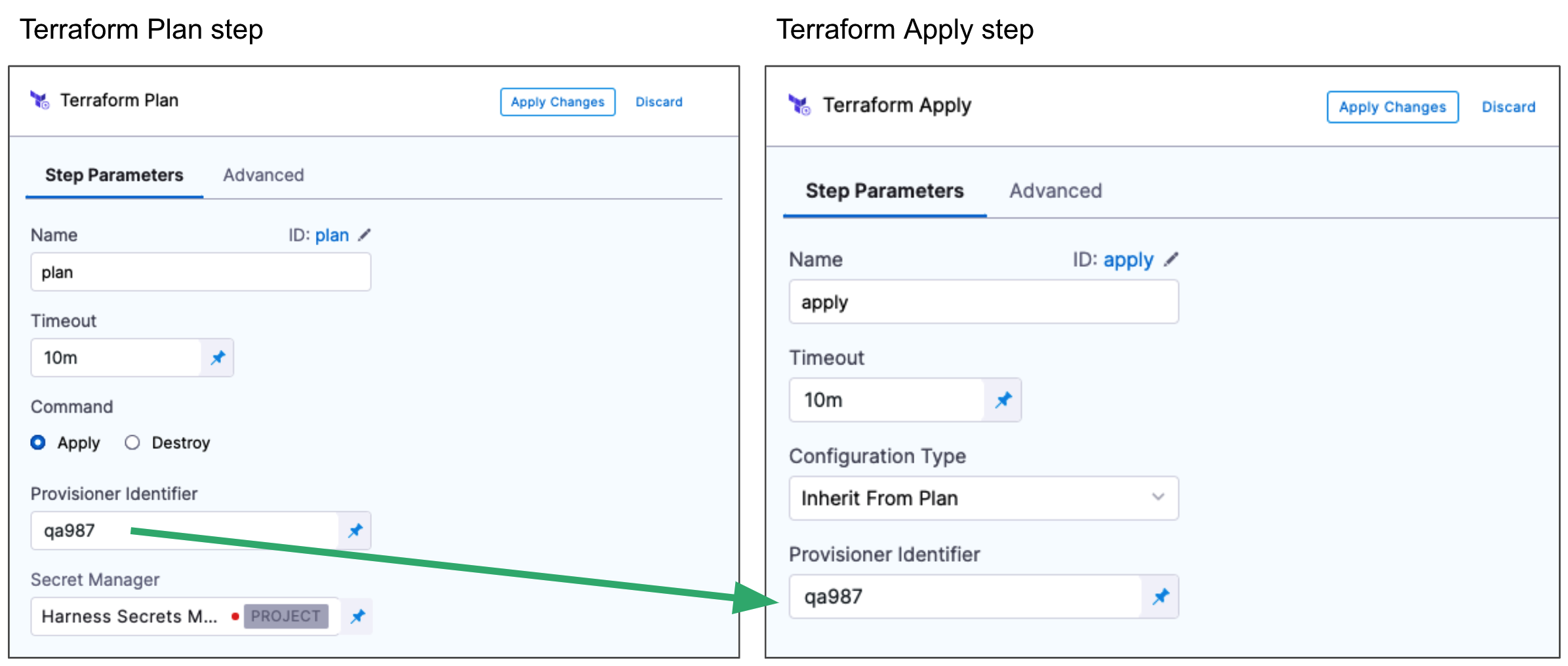
Typically the Terraform Plan step is used with the Terraform Apply step.
First, you add the Terraform Plan step and define the Terraform script for it to use.
Next, you add the Terraform Apply step, select Inherit from Plan in Configuration Type, and reference the Terraform Plan step using the same Provisioner Identifier.
For steps on using the Terraform Apply step, see:
You can also simply run the Terraform Plan without applying the plan using the Terraform Apply step.
Step 1: Add the Terraform Plan Step
In the Terraform Plan step, you connect Harness to your repo and add Terraform scripts.
You can add the Terraform Plan step in the stage's Infrastructure in Dynamic Provisioning. Dynamic Provisioning is used to provision the target infrastructure for the stage's deployment. Consequently, if you add Terraform Plan there, you must use a Terraform Apply step to apply the plan.
See Provision Target Deployment Infra Dynamically with Terraform.
You can also add a Terraform Plan step anywhere in the Execution steps for the stage. In that case, you aren't required to use a Terraform Apply step.
The Terraform Plan step has the following settings.
Name
In Name, enter a name for the step, for example, plan.
The name is very important. It's used to refer to settings in this step.
For example, if the name of the stage is Terraform and the name of the step is plan, and you want to echo its timeout setting, you would use:
<+pipeline.stages.Terraform.spec.execution.steps.plan.timeout>
Timeout
In Timeout, enter how long Harness should wait to complete the Terraform Plan step before failing the step.
Run on Remote Workspace
Currently, this feature is behind the feature flag CD_TERRAFORM_CLOUD_CLI_NG. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
Enable this option to identify whether the Terraform configuration uses a Terraform remote backend.
When enabled, you cannot provide the workspace input in Harness. The workspace will be outlined in your configuration for the remote backend.
Also, the remote backend is supported only when the Configuration Type is Inline.
terraform {
backend "remote" {
hostname = "app.terraform.io"
organization = "your-organization"
workspaces {
name = "your-workspace"
}
}
}
Command
In Command, select Apply or Destroy.
- Apply: The plan will be applied by a Terraform Apply step later in your stage. Even though you are only running a Terraform plan in this step, you identify that this step can be used with a Terraform Apply step later.
- Destroy: The plan will be applied by a Terraform Destroy step later in your stage.
Provisioner Identifier
Enter a unique value in Provisioner Identifier.
The Provisioner Identifier identifies the provisioning done in this step. You use the Provisioner Identifier in additional steps to refer to the provisioning done in this step.
The most common use of Provisioner Identifier is between the Terraform Plan and Terraform Apply steps. For the Terraform Apply step, to apply the provisioning from the Terraform Plan step, you use the same Provisioner Identifier.
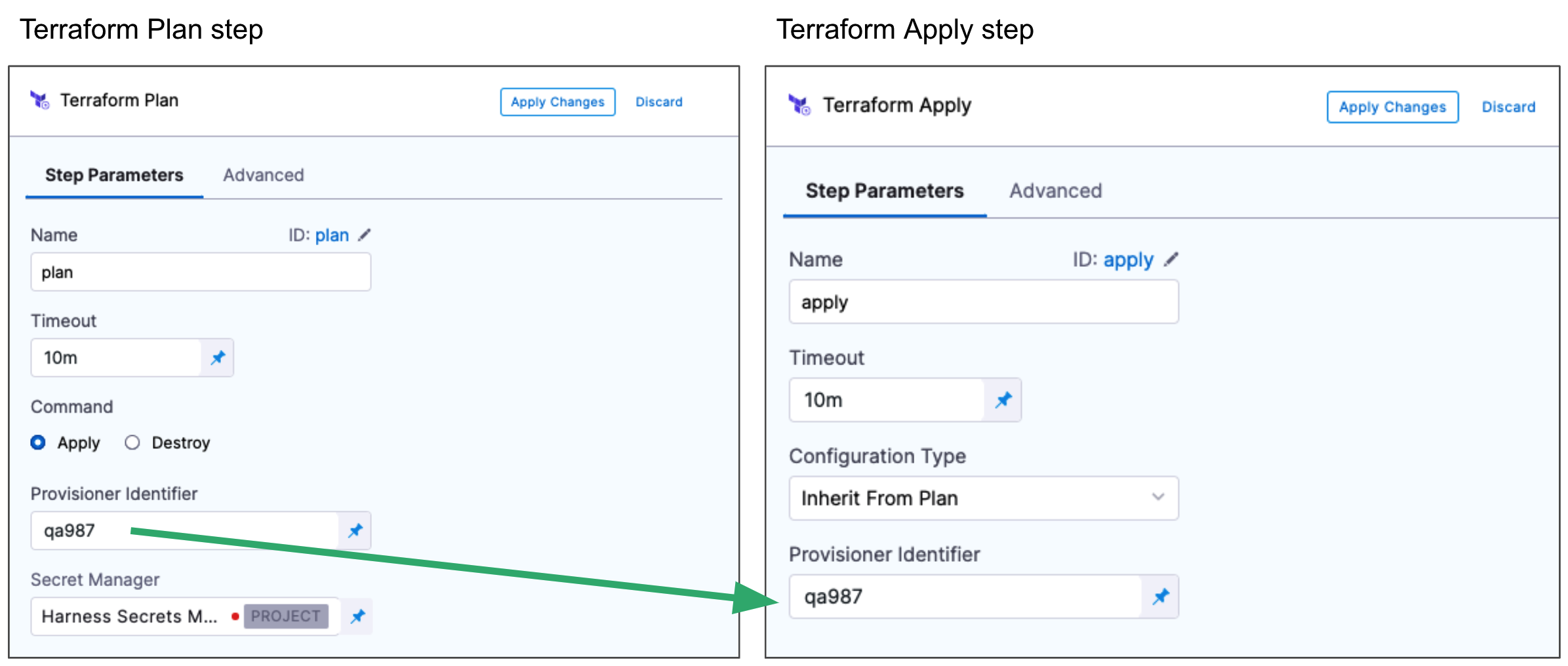
You also use the same Provisioner Identifier with the Terraform Destroy step to remove the provisioned resources.
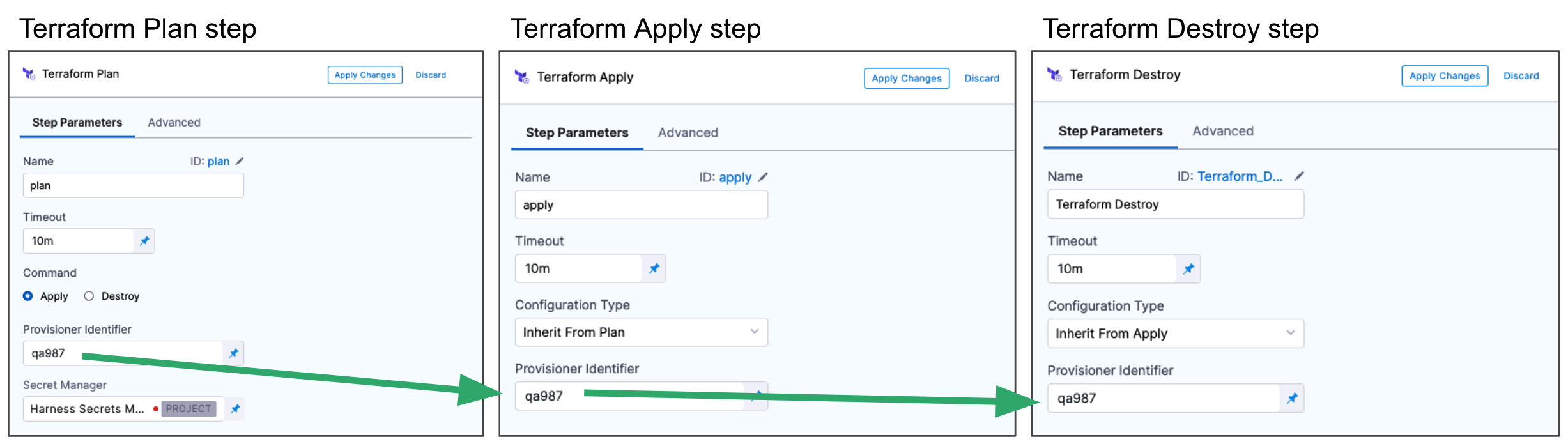
You also use the same Provisioner Identifier with the Terraform Rollback step to rollback the provisioned resources.
Provisioner Identifier Scope
The Provisioner Identifier is a Project-wide setting. You can reference it across Pipelines in the same Project.
For this reason, it's important that all your Project members know the Provisioner Identifiers. This will prevent one member building a Pipeline from accidentally impacting the provisioning of another member's Pipeline.
Secret Manager
Select a Secrets Manager to use for encrypting/decrypting and saving the Terraform plan file.
See Harness Secrets Manager Overview.
A Terraform plan is a sensitive file that could be misused to alter resources if someone has access to it. Harness avoids this issue by never passing the Terraform plan file as plain text.
Harness only passes the Terraform plan between the Harness Manager and Delegate as an encrypted file using a Secrets Manager.
When the terraform plan command runs on the Harness Delegate, the Delegate encrypts the plan and saves it to the Secrets Manager you selected. The encrypted data is passed to the Harness Manager.
When the plan is applied, the Harness Manager passes the encrypted data to the Delegate.
The Delegate decrypts the encrypted plan and applies it using the terraform apply command.
Limitations
The Terraform plan size must not exceed the secret size limit for secrets in your default Harness secret manager. For example, the AWS secrets manager has a limitation of 64KB. Other supported secrets managers support larger file sizes, typically, 256KB.
Configuration File Repository
Configuration File Repository is where the Terraform script and files you want to use are located.
Here, you'll add a connection to the Terraform script repo.
Click Specify Config File or edit icon.
The Terraform Config File Store settings appear.
Click the provider where your files are hosted.

Select or create a Connector for your repo. For steps, see Connect to a Git Repo or Artifactory Connector Settings Reference (see Artifactory with Terraform Scripts and Variable Definitions (.tfvars) Files).
In Git Fetch Type, select Latest from Branch or Specific Commit ID. When you run the Pipeline, Harness will fetch the script from the repo.
Specific Commit ID also supports Git tags. If you think the script might change often, you might want to use Specific Commit ID. For example, if you are going to be fetching the script multiple times in your Pipeline, Harness will fetch the script each time. If you select Latest from Branch and the branch changes between fetches, different scripts are run.
In Branch, enter the name of the branch to use.
In Folder Path, enter the path from the root of the repo to the folder containing the script.
For example, here's a Terraform script repo, the Harness Connector to the repo, and the Config Files settings for the branch and folder path:
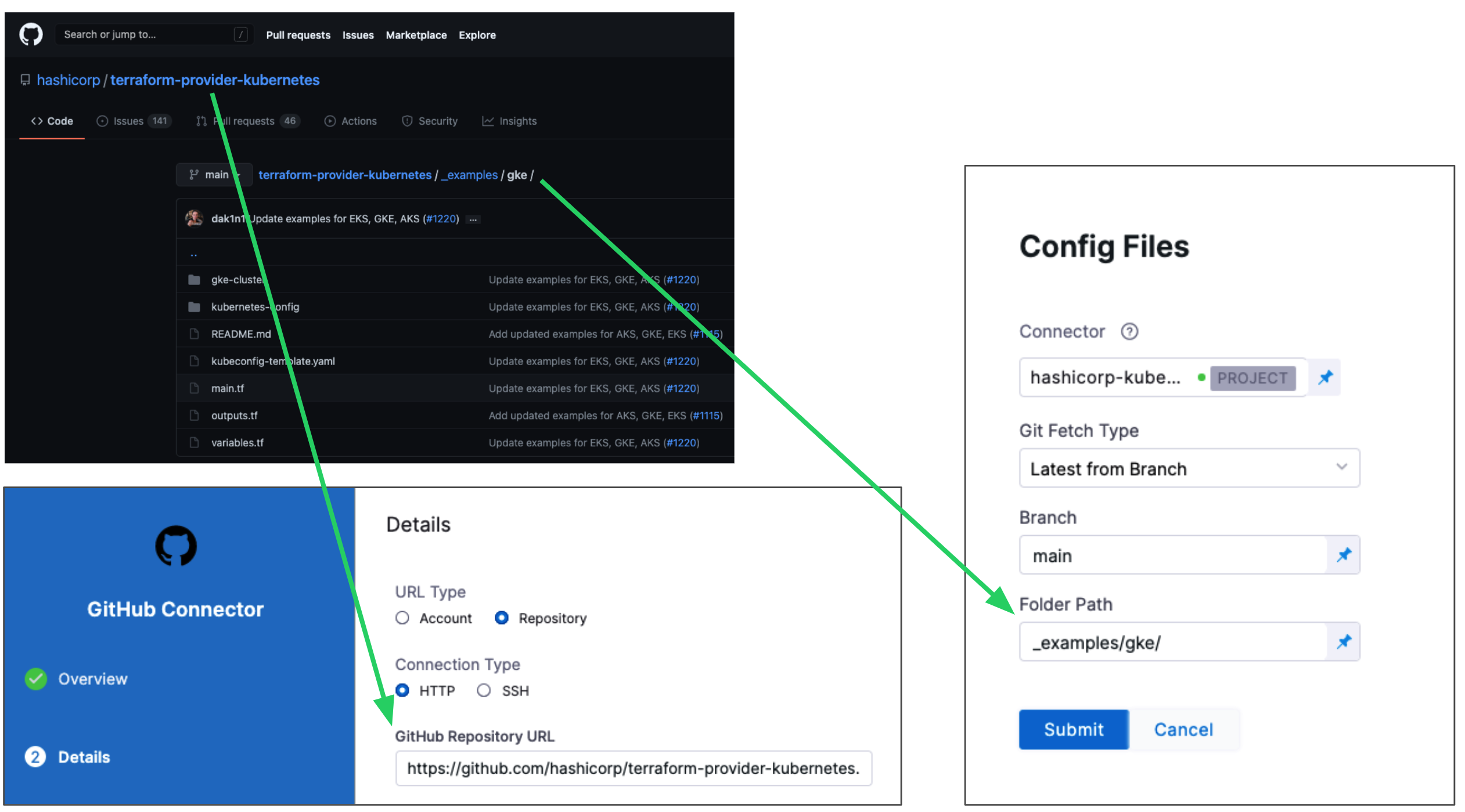
Click Submit.
Your Terraform Plan step is now ready. You can now configure a Terraform Apply, Destory, or Rollback step that can use the Terraform script from this Terraform Plan step.
The following sections cover common Terraform Plan step options.
Artifactory
See Artifactory Connector Settings Reference (see Artifactory with Terraform Scripts and Variable Definitions (.tfvars) Files).
AWS S3
In Region, select the region where your bucket is stored.
In Bucket, select the bucket where your Terraform files are stored (all buckets from the selected region that are available to the connector will be fetched).
In Folder Path, enter the path from the root of the repo to the folder containing the script.
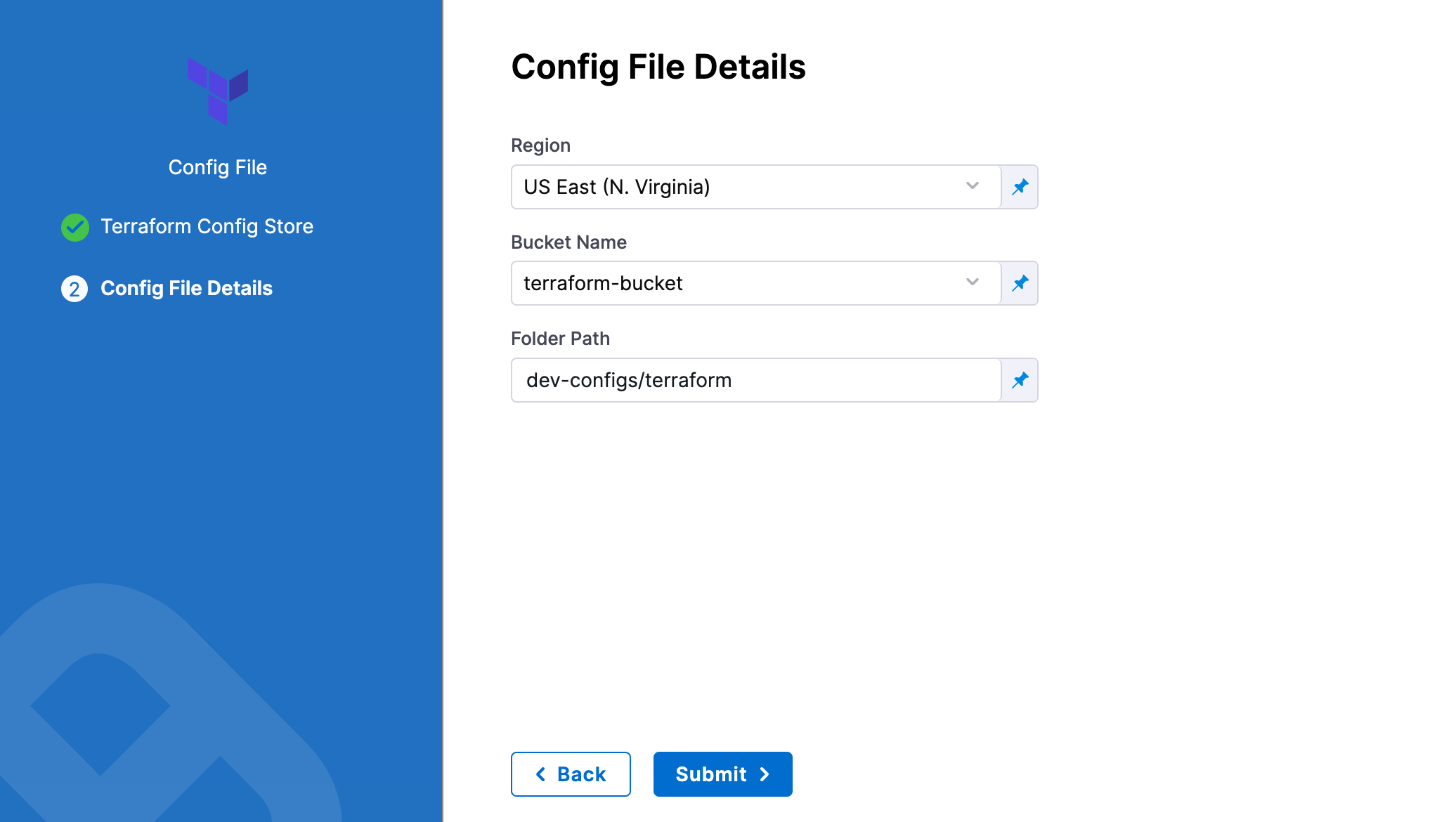
Harness will fetch all files from specified folder.
Source Module
When you set up the file repo in Configuration File Repository, you use a Harness Connector to connect to the repo where the Terraform scripts are located.
Some scripts will reference module sources in other repos and Harness will pull the source code for the desired child module at runtime (during terraform init).
In Source Module, you can select Use Connector credentials to have Harness use the credentials of the Connector to pull the source code for the desired child module(s).
If you do not select Use Connector credentials, Terraform will use the credentials that have been set up in the system.
The Use Connector credentials setting is limited to Harness Git Connectors using SSH authentication (not HTTPS) and a token.
When configuring the SSH key for the connector, exporting an SSH key with a passphrase for the module source is not supported. Configure an SSH Key without the passphrase.
Here are some syntax examples to reference the Terraform module using the SSH protocol:
source = "git@github.com:your-username/your-private-module.git"
## Workspace
Harness supports Terraform [workspaces](https://www.terraform.io/docs/state/workspaces.html). A Terraform workspace is a logical representation of one your infrastructures, such as Dev, QA, Stage, Production.
Workspaces are useful when testing changes before moving to a production infrastructure. To test the changes, you create separate workspaces for Dev and Production.
A workspace is really a different state file. Each workspace isolates its state from other workspaces. For more information, see [When to use Multiple Workspaces](https://www.terraform.io/docs/state/workspaces.html#when-to-use-multiple-workspaces) from Hashicorp.
Here's an example script where a local value names two workspaces, **default** and **production**, and associates different instance counts with each:
```json
locals {
counts = {
"default"=1
"production"=3
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "my_service" {
ami="ami-7b4d7900"
instance_type="t2.micro"
count="${lookup(local.counts, terraform.workspace, 2)}"
tags {
Name = "${terraform.workspace}"
}
}
In the workspace interpolation sequence, you can see the count is assigned by applying it to the Terraform workspace variable (terraform.workspace) and that the tag is applied using the variable also.
Harness will pass the workspace name you provide to the terraform.workspace variable, thus determining the count. If you provide the name production, the count will be 3.
In the Workspace setting, you can simply select the name of the workspace to use.
You can also use a stage variable in Workspace.
Later, when the Pipeline is deployed, you specify the value for the stage variable and it is used in Workspace.
This allows you to specify a different workspace name each time the Pipeline is run.
You can even set a Harness Trigger where you can set the workspace name used in Workspace.
Terraform Var Files
The Terraform Var Files section is for entering and/or linking to Terraform script Input variables.
You can use inline or remote var files.
Harness supports all Terraform input types and values.
Inline Variables
You can add inline variables just like you would in a tfvar file.
Click Add Terraform Var File, and then click Add Inline.
The Add Inline Terraform Var File settings appear.
In Identifier, enter an identifier so you can refer to variables using expressions if needed.
For example, if the Identifier is myvars you could refer to its content like this:
<+pipeline.stages.MyStage.spec.infrastructure.infrastructureDefinition.provisioner.steps.plan.spec.configuration.varFiles.myvars.spec.content>
Provide the input variables and values for your Terraform script. Harness follows the same format as Terraform.
For example, if your Terraform script has the following:
variable "region" {
type = string
}
In Add Inline Terraform Var File, you could enter:
region = "asia-east1-a"
Inline Variable Secrets
If you are entering secrets (for credentials, etc.), use Harness secret references in the value of the variable:
secrets_encryption_kms_key = "<+secrets.getValue("org.kms_key")>"
See Add Text Secrets.
Remote Variables
You can connect Harness to remote variable files.
Click Add Terraform Var File, and then click Add Remote.
Select your Git provider (GitHub, etc.) and then select or create a Connector to the repo where the files are located. Typically, this is the same repo where your Terraform script is located, so you can use the same Connector.
Click Continue. The Var File Details settings appear.
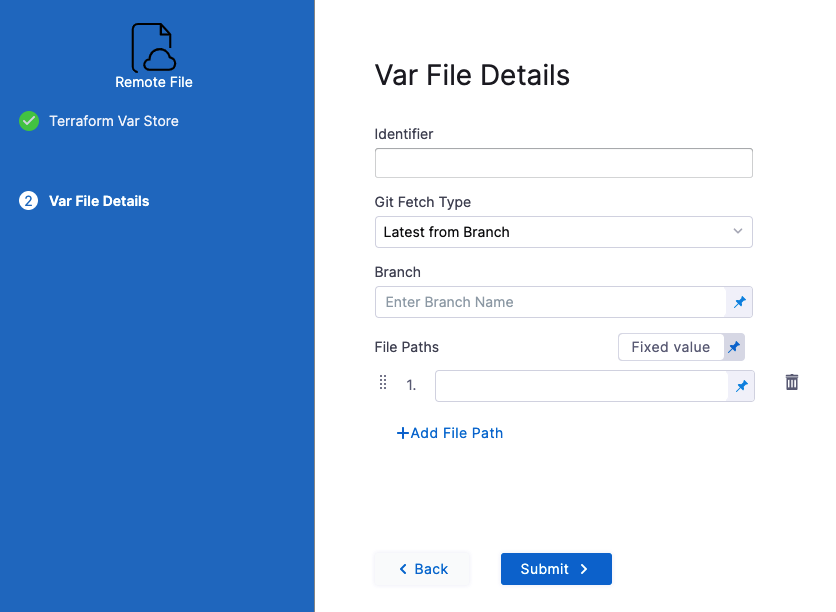
In Identifier, enter an identifier so you can refer to variables using expressions if needed.
For example, if the Identifier is myremotevars you could refer to its content like this:
<+pipeline.stages.MyStage.spec.infrastructure.infrastructureDefinition.provisioner.steps.plan.spec.configuration.varFiles.myremotevars.spec.store.spec.paths>
In Git Fetch Type, select Latest from Branch or Specific Commit ID.
In Branch, enter the name of the branch.
In File Paths, add one or more file paths from the root of the repo to the variable file.
Click Submit. The remote file(s) are added.
Artifactory
See Artifactory Connector Settings Reference (see Artifactory with Terraform Scripts and Variable Definitions (.tfvars) Files).
AWS S3
In Identifier, enter an identifier, so you can refer to variables using expressions if needed.
In Region, select the region where your bucket is stored.
In Bucket, select the bucket where your Terraform var files are stored (all buckets from the selected region that are available to the connector will be fetched).
In File Paths, add one or more file paths from the root of the bucket to the variable file.
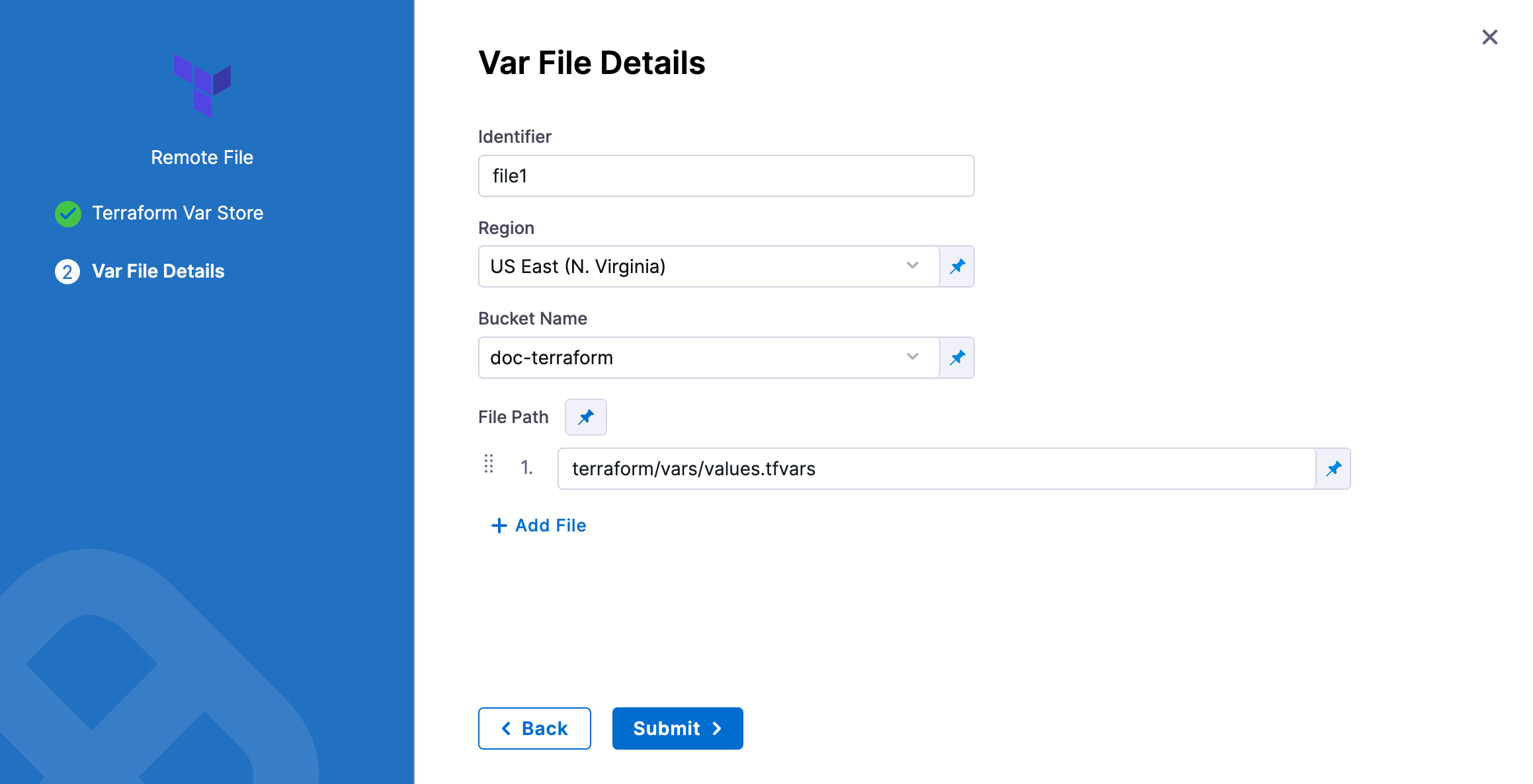
Click Submit. The remote file(s) are added.
Backend Configuration
The Backend Configuration section contains the remote state values.
You can use an inline or remote state file.
Using a remote Backend Config File
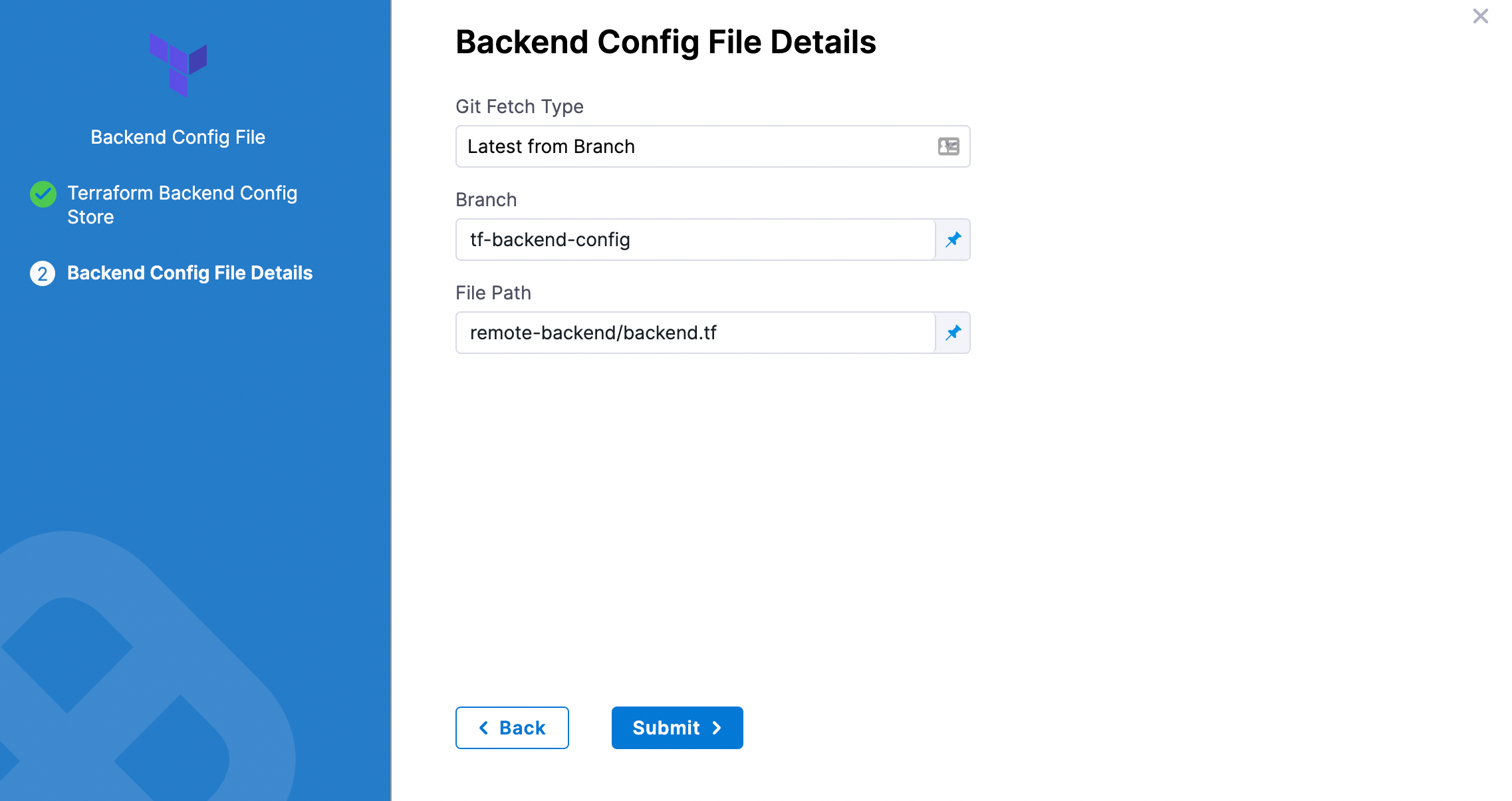
- In Backend Configuration, select Remote.
- Click Specify Backend Config File
- Select your provider (GitHub, Artifactory, S3, etc.) and then select or create a Connector to the repo where the files are located. Typically, this is the same repo where your Terraform script is located, so you can use the same Connector.
Git providers
In Git Fetch Type, select Latest from Branch or Specific Commit ID.
In Branch, enter the name of the branch.
In File Path, add file path from the root of the repo to the backend config file.
Click Submit. The remote file(s) are added.
Artifactory
See Artifactory Connector Settings Reference (see Artifactory with Terraform Scripts and Variable Definitions (.tfvars) Files).
AWS S3
In Region, select the region where your bucket is stored.
In Bucket, select the bucket where your backend config file is stored (all buckets from the selected region that are available to the connector will be fetched).
In File Path, add file path from the root of the bucket to the backend config file.
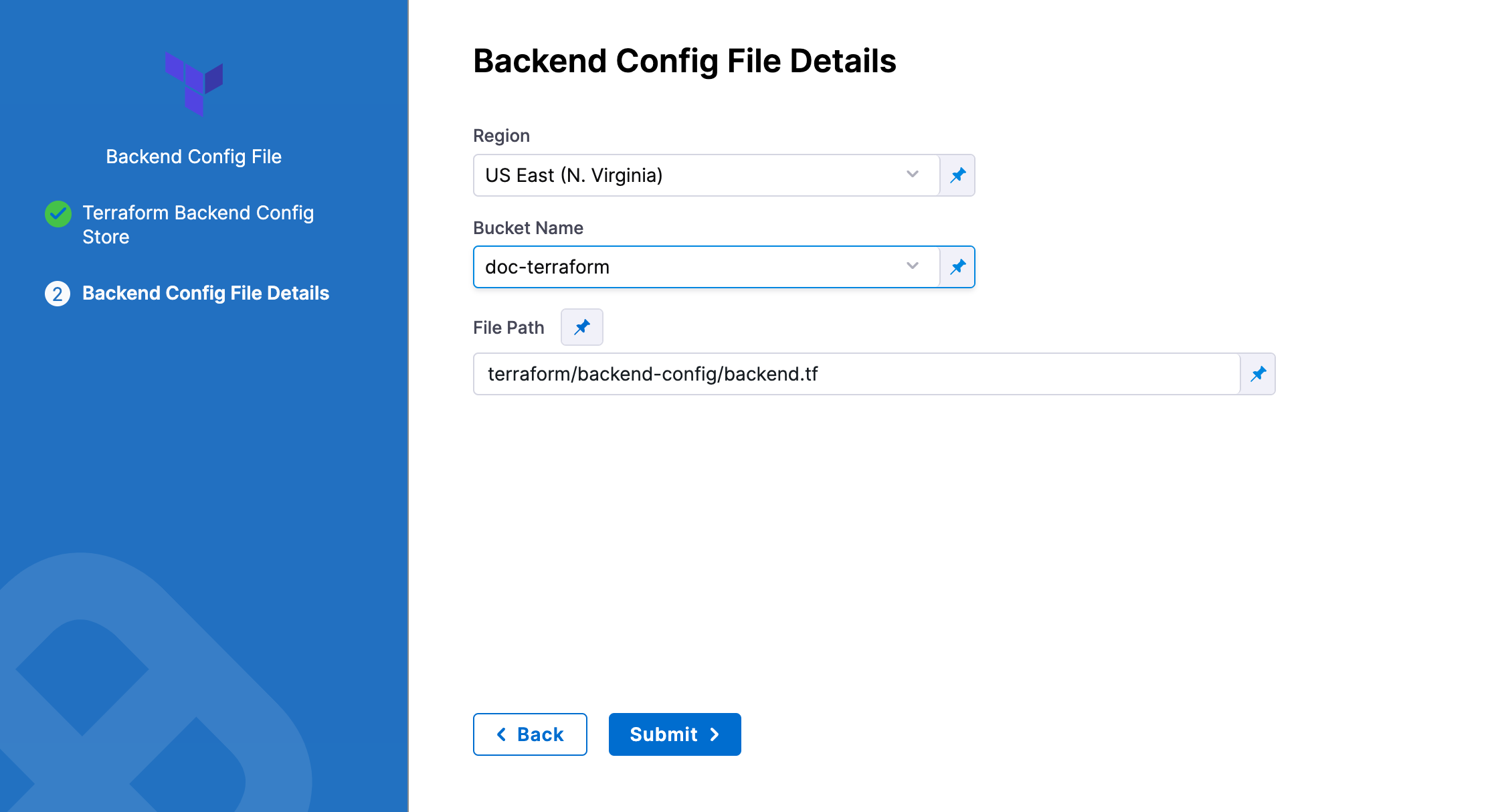
You can also use files in the Harness File Store.
To use the same remote state file set in the Terraform Plan step, Terraform Apply steps must use the same Provisioner Identifier.
For an example of how the config file should look, please see Backend Configuration from HashiCorp.
Here's an example.
main.tf (note the empty backend S3 block):
variable "global_access_key" {type="string"}
variable "global_secret_key" {type="string"}
variable "env" {
default= "test"
}
provider "aws" {
access_key = "${var.global_access_key}"
secret_key = "${var.global_secret_key}"
region = "us-east-1"
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "bucket" {
bucket = "prannoy-test-bucket"
}
terraform {
backend "s3" {
}
}
backend.tf:
access_key = "1234567890"
secret_key = "abcdefghij"
bucket = "terraform-backend-config-test"
key = "remotedemo.tfstate"
region = "us-east-1"
Using Inline State
Enter values for each backend config (remote state variable).
For example, if your config.tf file has the following backend:
terraform {
backend "gcs" {
bucket = "tf-state-prod"
prefix = "terraform/state"
}
}
In Backend Configuration, you provide the required configuration variables for the backend type.
For a remote backend configuration, the variables should be in .tfvars file.
Example:
bucket = "tf-state-prod"
prefix = "terraform/state"
In your Terraform .tf config file, only the definition of the Terraform backend is required:
terraform {
backend "gcs" {}
}
See Configuration variables in Terraform's gcs Standard Backend doc.
Targets
You can use the Targets setting to target one or more specific modules in your Terraform script, just like using the terraform plan -target command. See Resource Targeting from Terraform.
You simply identify the module using the standard format module.name, like you would using terraform plan -target="module.s3_bucket".
If you have multiple modules in your script and you don't select one in Targets, all modules are used.
Environment Variables
If your Terraform script uses environment variables, you can provide values for those variables here.
For example:
TF_LOG_PATH=./terraform.log
TF_VAR_alist='[1,2,3]'
You can use Harness encrypted text for values. See Add Text Secrets.
Export JSON representation of Terraform Plan
Enable this setting to use a JSON representation of the Terraform plan that is implemented in a Terraform Plan step.
In subsequent Execution steps, such as a Shell Script step, you can reference the Terraform plan using this expression format:
<+execution.steps.[Terraform Plan step Id].plan.jsonFilePath>
For example, if you had a Terraform Plan step with the Id Plan_Step, you could use the expression in a Shell Script step like this:
cat "<+execution.steps.Plan_Step.plan.jsonFilePath>"
If the Terraform Plan step is located in Dynamic Provisioning steps in Infrastructure, and the Terraform Plan step Id is TfPlan, then expression is:
<+infrastructure.infrastructureDefinition.provisioner.steps.TfPlan.plan.jsonFilePath>
For information on Terraform Plan in the Dynamic Provisioning steps in Infrastructure, see Provision Target Deployment Infra Dynamically with Terraform.JSON representation of Terraform plan can be accessed across different stages as well. In this case, the FQN for the step is required in the expression.
For example, if the Terraform Plan step with the Id TfPlan is in the Execution steps of a stage with the Id TfStage, then the expression is like this:
<+pipeline.stages.TfStage.spec.execution.steps.TfPlan.plan.jsonFilePath>
Scope of Expression
JSON representation of the Terraform plan is available only between the Terraform Plan step and subsequent Terraform Apply step. The expression will fail to resolve if used after the Terraform Apply step.
If used across stages, the Terraform Plan step can be used in one stage and the Terraform Apply step can be used in a subsequent stage. The expression will resolve successfully in this case.
The JSON of the Terraform Plan step is not available after Rollback.
Export Human Readable representation of Terraform Plan
Enable this option to view the Terraform plan file path and contents as human-readable JSON is subsequent steps, such as a Shell Script step.
Once you enable this option and run a CD stage with the Terraform Plan step, you can click in the Terraform Plan step's Output tab and copy the Output Value for the humanReadableFilePath output.
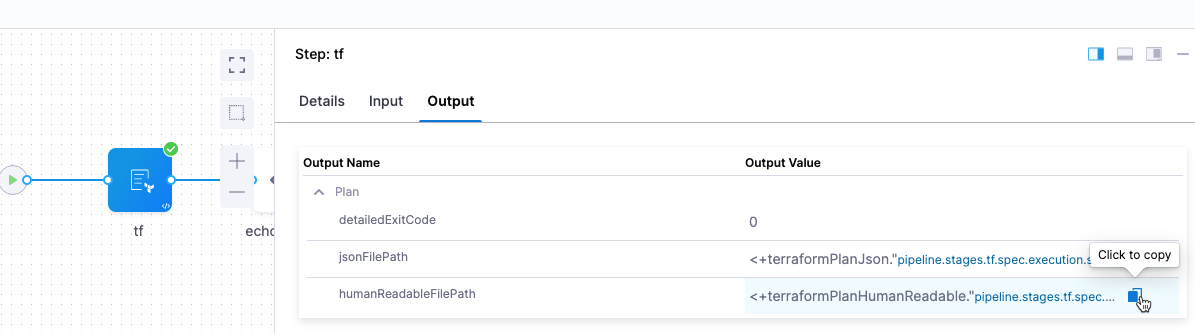
The format for the expression is:
- humanReadableFilePath:
<+terraformPlanHumanReadable."pipeline.stages.[stage Id].spec.execution.steps.[step Id].tf_planHumanReadable">
For example, if the Terraform Plan stage and step Ids are tf then you would get the following expressions:
- humanReadableFilePath:
<+terraformPlanHumanReadable."pipeline.stages.tf.spec.execution.steps.tf.tf_planHumanReadable">
Next, you can enter those expressions in a subsequent Shell Script step step and Harness will resolve them to the human-readable paths and JSON.
For example, here is a script using the variables:
echo "<+terraformPlanHumanReadable."pipeline.stages.tf.spec.execution.steps.tf.tf_planHumanReadable">"
echo "Plan is"
cat "<+terraformPlanHumanReadable."pipeline.stages.tf.spec.execution.steps.tf.tf_planHumanReadable">"
Note that if there are no changes in the plan, the standard Terraform message is shown in the Shell Step's logs:
No changes. Your infrastructure matches the configuration.
Terraform has compared your real infrastructure against your configuration
and found no differences, so no changes are needed.
Command line options
This setting allows you to set the Terraform CLI options for Terraform commands depending on the Terraform step type. For example: -lock=false, -lock-timeout=0s.
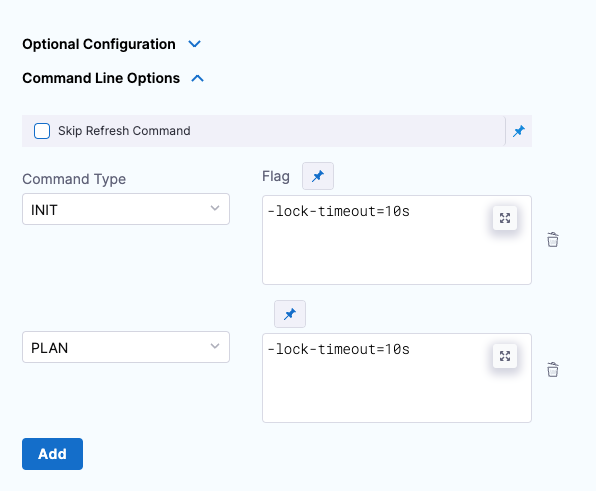
Skip Terraform Refresh
Terraform refresh command won't be running when this setting is selected.
Option: Terraform Plan detailed-exitcode
You can use the standard terraform plan command option detailed-exitcode with the Harness Terraform Plan step.
If you use the -detailed-exitcode option in a step that follows the Harness Terraform Plan step, such as a Shell Script step, Harness will return a detailed exit code:
0: succeeded with empty diff (no changes)1: error2: succeeded with non-empty diff (changes present)|
Exit codes are available as Terraform Plan step outputs that can be accessed using expressions with the following format:
<+pipeline.stages.STAGE_ID.spec.execution.steps.STEP_ID.plan.detailedExitCode>
For example:
<+pipeline.stages.TfStage.spec.execution.steps.TfPlan.plan.detailedExitCode>
Option: Advanced Settings
In Advanced, you can use the following options: