Pod API latency
Introduction
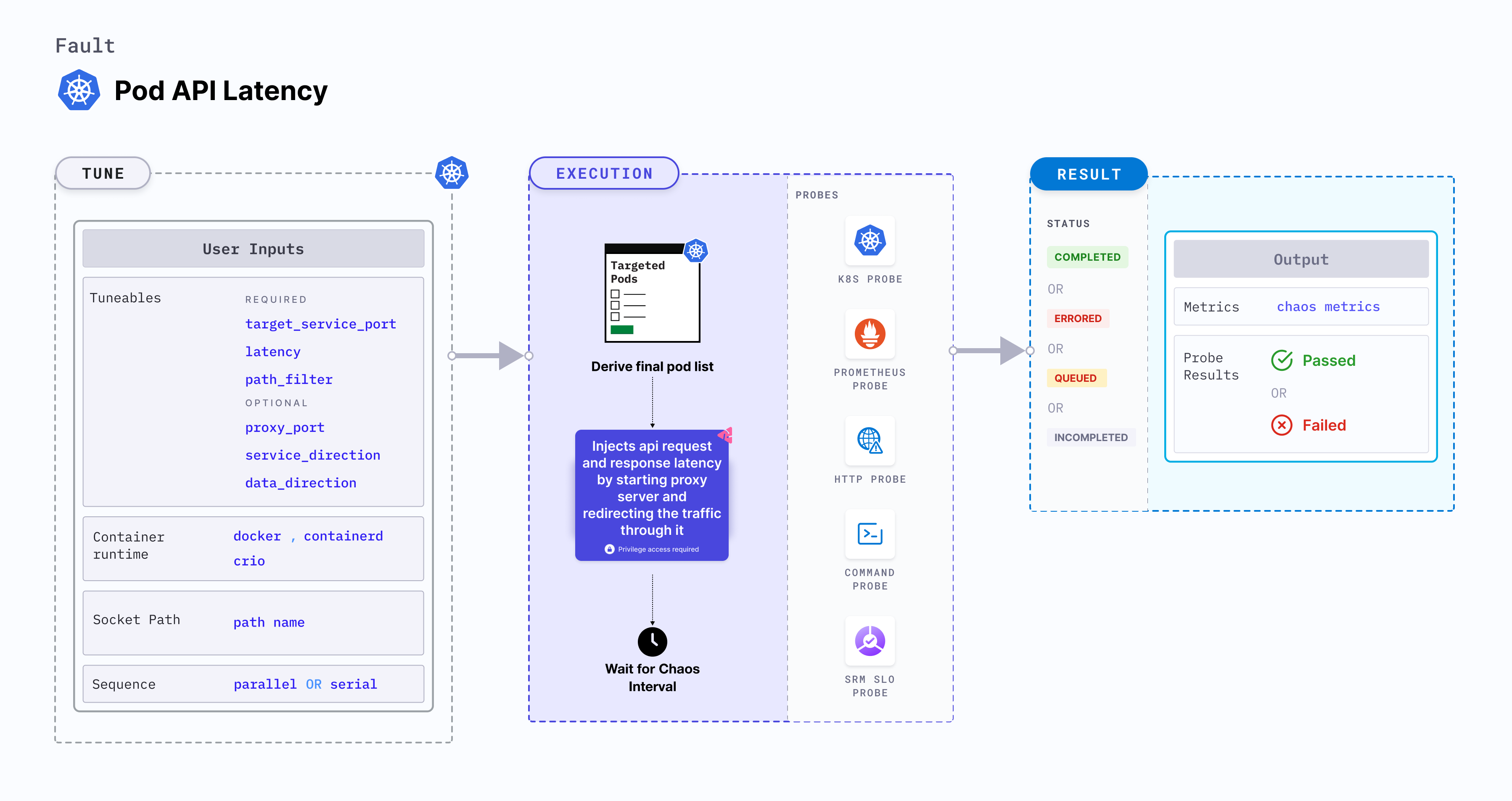
Pod API latency is a Kubernetes pod-level chaos fault that injects api request and response latency by starting proxy server and redirecting the traffic through it.
Use cases
Pod API latency:
- Simulate high traffic scenarios and testing the resilience and performance of an application or API, where the API may experience delays due to heavy load.
- Simulate situations where an API request takes longer than expected to respond. By introducing latency, you can test how well your application handles timeouts and implements appropriate error handling mechanisms.
- It can be used to test, how well the application handles network delays and failures, and if it recovers gracefully when network connectivity is restored.
- Kubernetes > 1.16 is required to execute this fault.
- The application pods should be in the running state before and after injecting chaos.
Fault tunables
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TARGET_SERVICE_PORT | Port of the target service. | Default: port 80. For more information, go to target service port |
| LATENCY | Delay added to the api requests and responses (in seconds). | Default: 2. For more information, go to latency |
| PATH_FILTER | Api path or route used for the filtering | For more information, go to path filter |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| PROXY_PORT | Port where the proxy listens for requests. | Default: 20000. For more information, go to proxy port |
| SERVICE_DIRECTION | Direction of the flow of control, ingress or egress | Default: `ingress`. For more information, go to service direction |
| DATA_DIRECTION | API payload type, request or response | Default: `both`. For more information, go to data direction |
| NETWORK_INTERFACE | Network interface used for the proxy. | Default: `eth0`. For more information, go to network interface |
| CONTAINER_RUNTIME | Container runtime interface for the cluster. | Default: containerd. Supports docker, containerd and crio. For more information, go to container runtime |
| SOCKET_PATH | Path to the containerd/crio/docker socket file. | Default: /run/containerd/containerd.sock. For more information, go to socket path |
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration to inject chaos (in seconds). | Default: 60s. For more information, go to duration of the chaos |
| TARGET_PODS | Comma-separated list of application pod names subject to pod HTTP latency. | If not provided, the fault selects target pods randomly based on provided appLabels. For more information, go to target specific pods |
| PODS_AFFECTED_PERC | Percentage of total pods to target. Provide numeric values. | Default: 0 (corresponds to 1 replica). For more information, go to pod affected percentage |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30 s. For more information, go to ramp time |
| SEQUENCE | Sequence of chaos execution for multiple target pods. | Default: parallel. Supports serial and parallel. For more information, go to sequence of chaos execution |
Target service port
Port of the target service. Tune it by using the TARGET_SERVICE_PORT environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the port of the targeted service
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-api-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
- name: PATH_FILTER
value: '/status'
Latency
Delay added to the API request and response. Tune it by using the LATENCY environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the latency value
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-api-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the latency value
- name: LATENCY
value: "2000"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
- name: PATH_FILTER
value: '/status'
Path Filter
API sub path/route to filter the api calls. Tune it by using the PATH_FILTER environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide api path filter
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-api-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the api path filter
- name: PATH_FILTER
value: '/status'
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Destination ports
A comma-separated list of the destination service or host ports for which egress traffic should be affected as a result of chaos testing on the target application. Tune it by using the DESTINATION_PORTS environment variable.
It is applicable only for the egress SERVICE_DIRECTION.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide destination ports
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-api-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# provide destination ports
- name: DESTINATION_PORTS
value: '80,443'
# provide the api path filter
- name: PATH_FILTER
value: '/status'
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
HTTPS enabled
This item is employed to facilitate HTTPS for both incoming and outgoing traffic, and its usage can vary depending on whether it's applied to ingress or egress scenarios. Tune it by using the HTTPS_ENABLED environment variable.
When applied to
ingresstraffic, it should be configured astrueif the HTTPS URL of the target application includes a port, following the formathttps://<hostname>:port. However, for HTTPS URLs in the form ofhttps://<hostname>without a port, this setting is not required.For egress traffic, setting it to
trueis necessary to enable HTTPS support for external services, which will then establish TLS certificates for the proxy within the target application.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## enable https support
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-api-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# enable https support
- name: HTTPS_ENABLED
value: 'true'
# provide the api path filter
- name: PATH_FILTER
value: '/status'
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Advanced fault tunables
PROXY_PORT: Port where the proxy listens for requests and responses.SERVICE_DIRECTION: Direction of the flow of control, either ingress or egress. It supportsingress,egressvalues.DATA_DIRECTION: API payload type, request, or response. It supportsrequest,response, andbothvalues.NETWORK_INTERFACE: Network interface used for the proxy.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# it injects the api latency fault
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-api-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the proxy port
- name: PROXY_PORT
value: '20000'
# provide the connection type
- name: SERVICE_DIRECTION
value: 'ingress'
# provide the payload type
- name: DATA_DIRECTION
value: 'both'
# provide the network interface
- name: NETWORK_INTERFACE
value: 'eth0'
# provide the api path filter
- name: PATH_FILTER
value: '/status'
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Container runtime and socket path
The CONTAINER_RUNTIME and SOCKET_PATH environment variables to set the container runtime and socket file path, respectively.
CONTAINER_RUNTIME: It supportsdocker,containerd, andcrioruntimes. The default value iscontainerd.SOCKET_PATH: It contains path of containerd socket file by default(/run/containerd/containerd.sock). Fordocker, specify path as/var/run/docker.sock. Forcrio, specify path as/var/run/crio/crio.sock.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of these environment variables:
## provide the container runtime and socket file path
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-api-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# runtime for the container
# supports docker, containerd, crio
- name: CONTAINER_RUNTIME
value: "containerd"
# path of the socket file
- name: SOCKET_PATH
value: "/run/containerd/containerd.sock"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
- name: PATH_FILTER
value: '/status'