Deploy using Kustomize
This tutorial helps you get started with Harness Continuous Delivery (CD). We will guide you through creating a CD pipeline and deployment of a Guestbook application. This Guestbook application will use Kustomize for deployment.
- CD pipeline
- GitOps workflow
You can choose to proceed with the tutorial either by using the command-line interface (Harness CLI) or the user interface (Harness UI).
- CLI
- UI
Before you begin
Complete the following tasks:
- Obtain a Harness API Token. For steps, go to the Harness documentation on creating a personal API token.
- Obtain a GitHub personal access token (PAT) with repo permissions. For steps, go to the GitHub documentation on creating a personal access token.
- Obtain a Kubernetes cluster. Use your own Kubernetes cluster. If you do not have one, we recommend that you use K3D for installing Harness delegates and deploying a sample application in a local development environment.
- Install Helm CLI.
- Fork the harnessed-example-apps repository through the GitHub web interface.
- For details on forking a GitHub repository, go to GitHub docs.
Getting Started with Harness CD
- Download and configure the Harness CLI.
- MacOS
- Linux
- Windows
curl -LO https://github.com/harness/harness-cli/releases/download/v0.0.13-alpha/harness-v0.0.13-alpha-darwin-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xvf harness-v0.0.13-alpha-darwin-amd64.tar.gz
echo 'export PATH="'$(pwd)':$PATH"' >> ~/.bash_profile
source ~/.bash_profile
- ARM
- AMD
curl -LO https://github.com/harness/harness-cli/releases/download/v0.0.13-alpha/harness-v0.0.13-alpha-linux-arm64.tar.gz
tar -xvf harness-v0.0.13-alpha-darwin-amd64.tar.gz
echo 'export PATH="'$(pwd)':$PATH"' >> ~/.bash_profile
source ~/.bash_profile
curl -LO https://github.com/harness/harness-cli/releases/download/v0.0.13-alpha/harness-v0.0.13-alpha-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xvf harness-v0.0.13-alpha-darwin-amd64.tar.gz
echo 'export PATH="'$(pwd)':$PATH"' >> ~/.bash_profile
source ~/.bash_profile
a. Open Windows Powershell and run the following command to download the Harness CLI.
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://github.com/harness/harness-cli/releases/download/v0.0.13-alpha/harness-v0.0.13-alpha-windows-amd64.zip -OutFile ./harness.zip
b. Extract the downloaded Zip file and change the directory to the extracted file location.
c. Perform the following steps to make it accessible through a terminal.
$currentPath = Get-Location
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$env:PATH;$currentPath", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)
d. Restart the terminal.
Clone the forked harnessed-example-apps repo and change the directory.
git clone https://github.com/GITHUB_ACCOUNTNAME/harnesscd-example-apps.git
cd harnesscd-example-appsNote: Replace
GITHUB_ACCOUNTNAMEwith your GitHub account name.Log in to Harness from the CLI.
harness login --api-key --account-id HARNESS_API_TOKENNote: Replace
HARNESS_API_TOKENwith the Harness API token that you obtained during the prerequisite section of this tutorial.
For the pipeline to run successfully, perform all of the following steps as they are, including the naming conventions.
Delegate
The Harness Delegate is a service that runs in your local network or VPC to establish connections between the Harness Manager and various providers such as artifact registries, cloud platforms, etc. The delegate is installed in the target infrastructure (Kubernetes cluster) and performs operations including deployment and integration. To learn more about the delegate, go to delegate overview.
Log in to the Harness UI. In Project Setup, select Delegates.
Select Delegates.
Select Install delegate. For this tutorial, let's explore how to install the delegate by using Helm.
Add the Harness Helm chart repo to your local Helm registry.
helm repo add harness-delegate https://app.harness.io/storage/harness-download/delegate-helm-chart/helm repo update harness-delegateRun the following command, replacing
ACCOUNT_ID,MANAGER_ENDPOINT, andDELEGATE_TOKENwith the corresponding auto-populated values from the delegate installation wizard.helm upgrade -i helm-delegate --namespace harness-delegate-ng --create-namespace \
harness-delegate/harness-delegate-ng \
--set delegateName=helm-delegate \
--set accountId=ACCOUNT_ID \
--set managerEndpoint=MANAGER_ENDPOINT \
--set delegateDockerImage=harness/delegate:23.03.78904 \
--set replicas=1 --set upgrader.enabled=false \
--set delegateToken=DELEGATE_TOKEN
Verify that the delegate is installed successfully and can connect to Harness Manager.
You can also follow the Install Harness delegate on Kubernetes or Docker tutorial to install the delegate using the Terraform Helm Provider or Kubernetes manifest.
Secrets
Harness offers built-in secret management for encrypted storage of sensitive information. Secrets are decrypted when needed, and only the private network-connected Harness delegate has access to the key management system. You can also integrate your own secret management solution. To learn more about secrets in Harness, go to Secrets Management.
Create a secret to store the GitHub PAT. This will be used in the next step to create a GitHub connector.
harness secret --token GITHUB_PAT applyNote: Replace
GITHUB_PATwith the GitHub PAT that you obtained during the prerequisite section of this tutorial.
Connectors
Connectors in Harness enable integration with third-party tools, providing connection and authentication at deployment runtime. For example, a GitHub connector facilitates authentication and fetching files from a GitHub repository within pipeline stages. To learn more about connectors, go to Connectors.
Create a GitHub connector.
harness connector --file kustomize-guestbook/harnesscd-pipeline/github-connector.yml apply --git-user GITHUB_ACCOUNTNAMECreate a Kubernetes connector.
harness connector --file kustomize-guestbook/harnesscd-pipeline/kubernetes-connector.yml apply --delegate-name helm-delegate
Environment
Environments determine the deployment location, categorized as Production and Pre-Production. Each environment includes infrastructure definitions for VMs, Kubernetes clusters, or target infrastructures. To learn more about environments, go to Environment Overview.
Create a Environment.
harness environment --file kustomize-guestbook/harnesscd-pipeline/environment.yml applyCreate a Infrastructure Definition.
harness infrastructure --file kustomize-guestbook/harnesscd-pipeline/infrastructure-definition.yml apply
Services
In Harness, services represent what you deploy to environments. You use services to configure variables, manifests, and artifacts. The Services dashboard provides service statistics like deployment frequency and failure rate. To learn more about services, go to Services Overview.
- Create a Service.
harness service --file kustomize-guestbook/harnesscd-pipeline/service.yml apply
Pipeline
A pipeline is a comprehensive process encompassing integration, delivery, operations, testing, deployment, and monitoring. It can utilize CI for code building and testing and follow that up with CD for artifact deployment in production. A CD pipeline is a series of stages where each stage deploys a service to an environment. To learn more about CD pipeline basics, go to CD pipeline basics.
- Canary
- Blue Green
- Rolling
A canary deployment updates nodes in a single environment gradually, allowing you to use gates between increments. Canary deployments allow incremental updates and ensure a controlled rollout process. For more information, go to When to use Canary deployments.
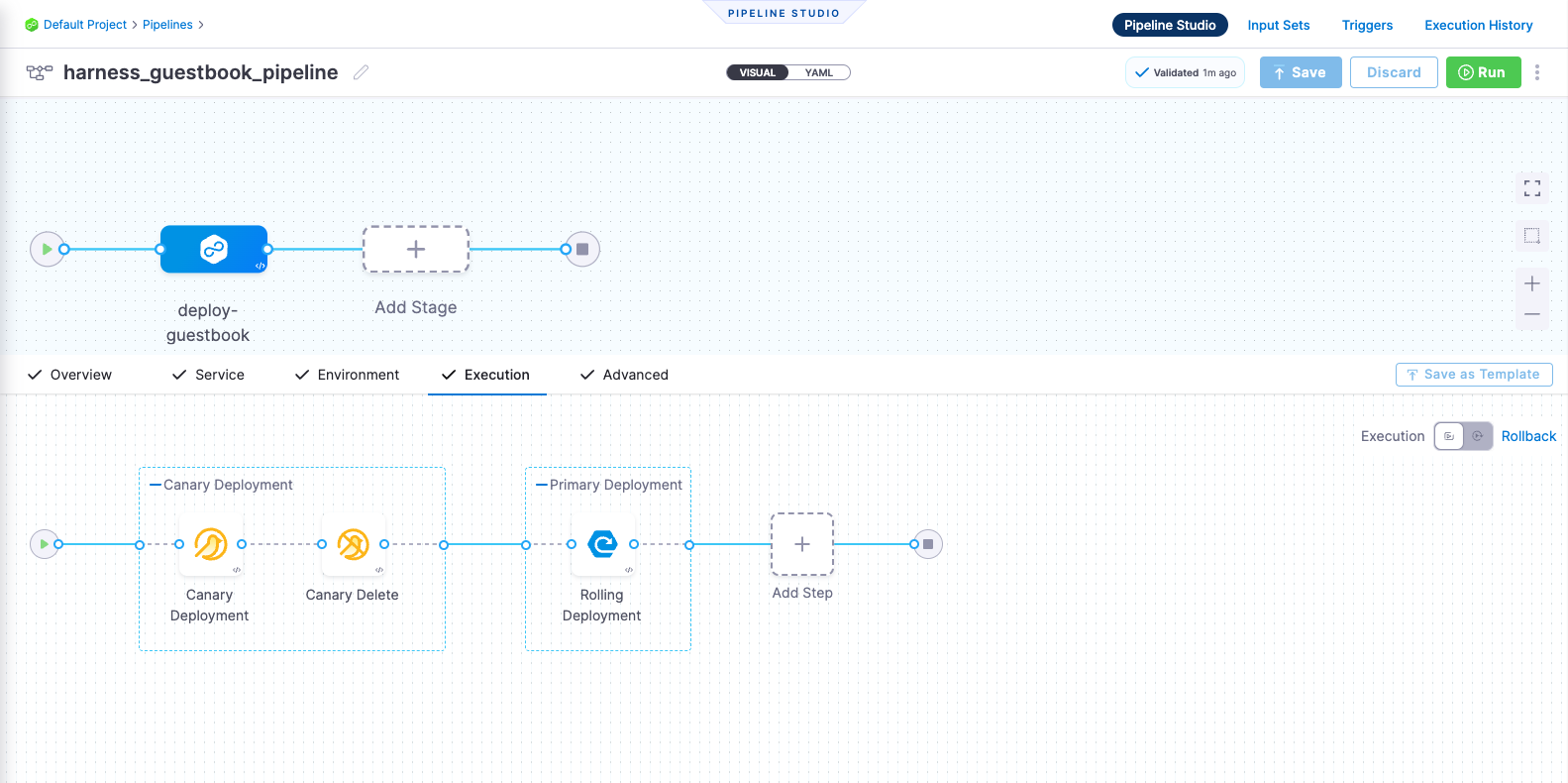
harness pipeline --file kustomize-guestbook/harnesscd-pipeline/canary-pipeline.yml apply
- You can confirm the pipeline, stage, and execution steps are as shown below in the Harness UI.
Blue Green deployments involve running two identical environments (stage and prod) simultaneously with different service versions. QA and UAT are performed on a new service version in the stage environment first. Next, traffic is shifted from the prod environment to stage, and the previous service version running on prod is scaled down. Blue Green deployments are also referred to as red/black deployment by some vendors. For more information, go to When to use Blue Green deployments.
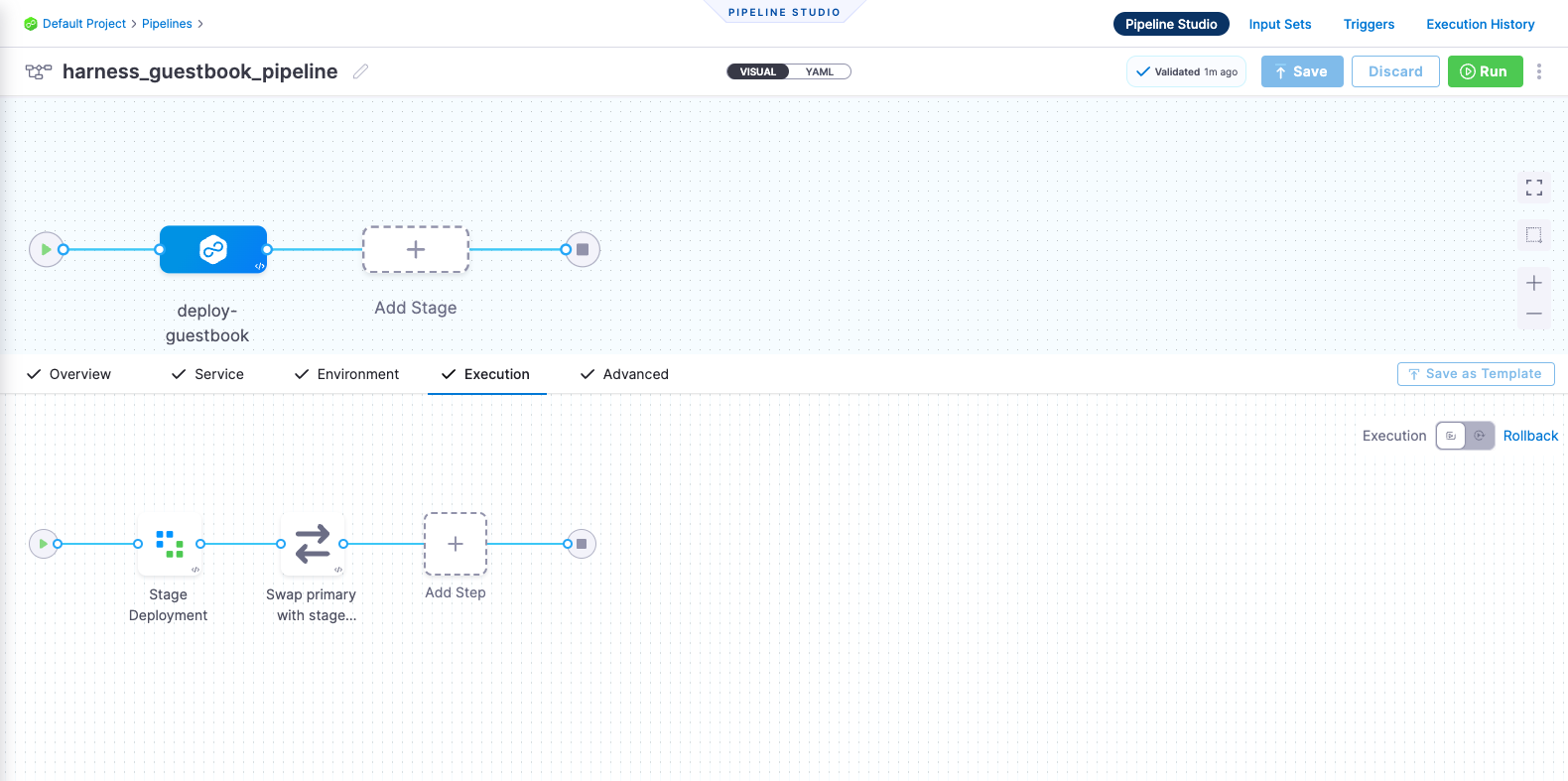
harness pipeline --file kustomize-guestbook/harnesscd-pipeline/bluegreen-pipeline.yml apply
- You can confirm the pipeline, stage, and execution steps are as shown below in the Harness UI.
Rolling deployments incrementally add nodes in a single environment with a new service version, either one node at a time or in batches defined by a window size. Rolling deployments allow a controlled and gradual update process for the new service version. For more information, go to When to use rolling deployments.
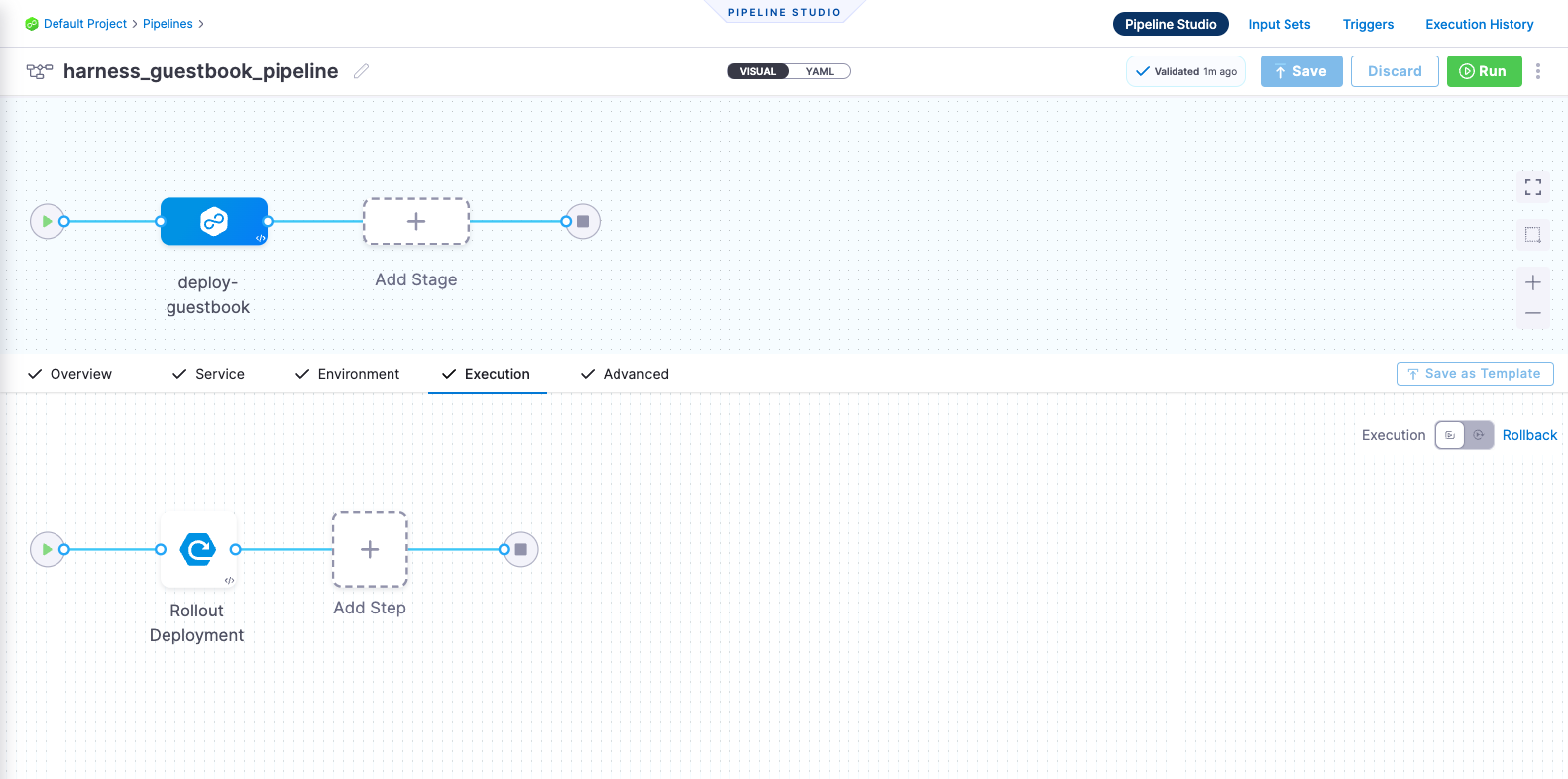
harness pipeline --file kustomize-guestbook/harnesscd-pipeline/rolling-pipeline.yml apply
- You can confirm the pipeline, stage, and execution steps are as shown below in the Harness UI.
Before you begin
Verify the following:
- Obtain GitHub personal access token with repo permissions. For steps, go to the GitHub documentation on creating a personal access token.
- A Kubernetes cluster. Use your own Kubernetes cluster or we recommend using K3D for installing Harness delegates and deploying a sample application in a local development environment.
- Install Helm CLI.
- Fork the harnessed-example-apps repository through the GitHub web interface.
- For details on forking a GitHub repository, go to GitHub docs.
Getting Started with Harness CD
Log into Harness.
Select Projects, and then select Default Project.
For the pipeline to run successfully, please follow all of the following steps as they are, including the naming conventions.
Delegate
The Harness Delegate is a service that runs in your local network or VPC to establish connections between the Harness Manager and various providers such as artifact registries, cloud platforms, etc. The delegate is installed in the target infrastructure (Kubernetes cluster) and performs operations including deployment and integration. To learn more about the delegate, go to delegate Overview.
In Project Setup, select Delegates.
Select Tokens.
- Select New Token.
- Enter the named
delegate_token. - Select Apply.
- Copy the token value by selecting the copy icon and store the token somewhere.
- Select Close.
Select Delegates.
Select Install delegate. For this tutorial, let's explore how to install the delegate using Helm.
Add the Harness Helm chart repo to your local Helm registry.
helm repo add harness-delegate https://app.harness.io/storage/harness-download/delegate-helm-chart/helm repo update harness-delegateIn the command provided,
ACCOUNT_ID,MANAGER_ENDPOINTandDELEGATE_TOKENare auto-populated values that you can obtain from the delegate Installation wizard.helm upgrade -i helm-delegate --namespace harness-delegate-ng --create-namespace \
harness-delegate/harness-delegate-ng \
--set delegateName=helm-delegate \
--set accountId=ACCOUNT_ID \
--set managerEndpoint=MANAGER_ENDPOINT \
--set delegateDockerImage=harness/delegate:23.03.78904 \
--set replicas=1 --set upgrader.enabled=false \
--set delegateToken=DELEGATE_TOKEN
Verify that the delegate is installed successfully and can connect to the Harness Manager.
You can also follow the Install Harness delegate on Kubernetes or Docker tutorial to install the delegate using the Terraform Helm Provider or Kubernetes manifest.
Secrets
Harness offers built-in secret management for encrypted storage of sensitive information. Secrets are decrypted when needed, and only the private network-connected Harness delegate has access to the key management system. You can also integrate your own secret management solution. To learn more about secrets in Harness, go to Secrets Management.
- In Project Setup, select Secrets.
- Select New Secret > Text.
- Enter the secret name
harness_gitpat. - For the secret value, paste in the GitHub Personal Access Token.
- Select Save.
Connectors
Connectors in Harness enable integration with 3rd party tools, providing connection and authentication at deployment runtime. For example, a GitHub connector facilitates authentication and fetching files from a GitHub repository within pipeline stages. To learn more about connectors, go to Connectors.
Create a GitHub connector.
- Copy the contents of github-connector.yml.
- In Harness, in Project Setup, select Connectors.
- Select Create via YAML Builder and paste the copied YAML.
- Assuming you have already forked the harnessed-example-apps repository as mentioned earlier, replace GITHUB_USERNAME with your GitHub account username in the YAML wherever required.
- Select Save Changes and verify that the new connector named harness_gitconnector is successfully created.
- Finally, select Test under CONNECTIVITY STATUS to ensure the connection is successful.
Create Kubernetes connector.
- Copy the contents of kubernetes-connector.yml.
- In Harness, in Project Setup, select Connectors.
- Select Create via YAML Builder and paste in the copied YAML.
- In the YAML, replace DELEGATE_NAME with the installed delegate name. To obtain the delegate name, navigate to Default Project > Project Setup > Delegates.
- Select Save Changes and verify that the new connector named harness_k8sconnector is successfully created.
- Finally, select Test under CONNECTIVITY STATUS to verify the connection is successful.
Environment
Environments determine the deployment location, categorized as Production and Pre-Production. Each environment includes infrastructure definitions for VMs, Kubernetes clusters, or target infrastructures. To learn more about environments, go to Environment Overview.
- In Default Project, select Environments.
- Select New Environment and toggle to YAML to use the YAML editor.
- Copy the contents of environment.yml and paste it into the YAML editor and select Save.
- In Infrastructure Definitions, select Infrastructure Definition and select Edit YAML.
- Copy the contents of infrastructure-definition.yml and paste it into the YAML editor.
- Select Save and verify that the environment and infrastructure definition is created successfully.
Services
In Harness, services represent what you deploy to environments. You use services to configure variables, manifests, and artifacts. The Services dashboard provides service statistics like deployment frequency and failure rate. To learn more about services, go to Services Overview.
- In Default Project, select Services.
- Select New Service.
- Name the service
harnessguestbook. - Select Save, and then in the Configuration tab, toggle to YAML to use the YAML editor.
- Select Edit YAML and copy the contents of service.yml and paste it into the YAML editor.
- Select Save and verify that the Service harness_guestbook is successfully created.
Pipeline
A pipeline is a comprehensive process encompassing integration, delivery, operations, testing, deployment, and monitoring. It can utilize CI for code building and testing, followed by CD for artifact deployment in production. A CD pipeline is a series of stages where each stage deploys a service to an environment. To learn more about CD pipeline basics, go to CD pipeline basics.
- Canary
- Blue Green
- Rolling
A canary deployment updates nodes in a single environment gradually, allowing you to use gates between increments. Canary deployments allow incremental updates and ensure a controlled rollout process. For more information, go to When to use Canary deployments.
In Default Project, select Pipelines.
- Select New Pipeline.
- Enter the name
guestbook_canary_pipeline. - Select Inline to store the pipeline in Harness.
- Select Start and, in the Pipeline Studio, toggle to YAML to use the YAML editor.
- Select Edit YAML to enable edit mode, and choose any of the following execution strategies. Paste the respective YAML based on your selection.
Copy the contents of canary-pipeline.yml and paste it into the YAML editor.
Select Save.
You can switch to the Visual editor and confirm the pipeline, stage, and execution steps are as shown below.

Blue Green deployments involve running two identical environments (stage and prod) simultaneously with different service versions. QA and UAT are performed on a new service version in the stage environment first. Next, traffic is shifted from the prod environment to stage, and the previous service version running on prod is scaled down. Blue Green deployments are also referred to as red/black deployment by some vendors. For more information, go to When to use Blue Green deployments.
In Default Project, select Pipelines.
- Select New Pipeline.
- Enter the name
guestbook_bluegreen_pipeline. - Select Inline to store the pipeline in Harness.
- Select Start and, in the Pipeline Studio, toggle to YAML to use the YAML editor.
- Select Edit YAML to enable edit mode, and choose any of the following execution strategies. Paste the respective YAML based on your selection.
Copy the contents of bluegreen-pipeline.yml and paste it into the YAML editor.
Select Save.
You can switch to the Visual editor and confirm the pipeline, stage, and execution steps are as shown below.

Rolling deployments incrementally add nodes in a single environment with a new service version, either one-by-one or in batches defined by a window size. Rolling deployments allow a controlled and gradual update process for the new service version. For more information, go to When to use rolling deployments.
In Default Project, select Pipelines.
- Select New Pipeline.
- Enter the name
guestbook_rolling_pipeline. - Select Inline to store the pipeline in Harness.
- Select Start and, in the Pipeline Studio, toggle to YAML to use the YAML editor.
- Select Edit YAML to enable edit mode, and choose any of the following execution strategies. Paste the respective YAML based on your selection.
Copy the contents of rolling-pipeline.yml and paste it into the YAML editor.
Select Save.
You can switch to the Visual editor and confirm the pipeline, stage, and execution steps are as shown below.

Finally, it's time to execute the pipeline. Select Run, and then select Run Pipeline to initiate the deployment.
Observe the execution logs as Harness deploys the workload and checks for steady state.
After a successful execution, you can check the deployment in your Kubernetes cluster using the following command:
kubectl get pods -n defaultTo access the Guestbook application deployed via the Harness pipeline, port forward the service and access it at http://localhost:8080:
kubectl port-forward svc/kustomize-guestbook-ui 8080:80
Congratulations!🎉
You've just learned how to use Harness CD to deploy an application using a Kustomize template.
What's Next?
- Keep learning about Harness CD. Add triggers to your pipeline that'll respond to Git events by following this guide.
- Visit the Harness Developer Hub for more Tutorials and resources.
How to deploy your own app by using Harness
You can integrate your own microservice application into this tutorial by following the steps outlined below:
Utilize the same delegate that you deployed as part of this tutorial. Alternatively, deploy a new delegate, but remember to use a newly created delegate identifier when creating connectors.
If you intend to use a private Git repository that hosts your Kustomize files, create a Harness secret containing the Git personal access token (PAT). Subsequently, create a new Git connector using this secret.
Create a Kubernetes connector if you plan to deploy your applications in a new Kubernetes environment. Make sure to update the infrastructure definition to reference this newly created Kubernetes connector.
Once you complete all the aforementioned steps, create a new Harness service that leverages Kustomize for deploying applications.
Lastly, establish a new deployment pipeline and select the newly created infrastructure definition and service. Choose a deployment strategy that aligns with your microservice application's deployment needs.
Voila! You're now ready to deploy your own application using Harness.
Whether you're new to GitOps or have already used Argo CD, this guide will assist you in getting started with Harness GitOps, both with and without Argo CD.
Harness also offers a Hosted GitOps solution, and a tutorial for it will be available soon.
Before you begin
Verify the following:
- A Kubernetes cluster. We recommend K3D for installing the Harness GitOps Agent and deploying a sample application in a local development environment.
- Fork the harnessed-example-apps repository through the GitHub web interface.
- For details on Forking a GitHub repository, go to GitHub docs.
Getting Started with Harness GitOps
Log in to the Harness App.
Select on Projects in the top left corner, choose Default Project.
Select Deployments, under Default Project select on GitOps.
GitOps Agent
A Harness GitOps Agent is a worker process that runs in your environment, makes secure, outbound connections to Harness, and performs all the GitOps tasks you request in Harness.
- Select Settings, and then select GitOps Agents.
- Select New GitOps Agent.
- When are prompted with Do you have any existing Argo CD instances?, select Yes if you already have a Argo CD Instance, or else choose No to install the Harness GitOps Agent.
- Harness GitOps Agent Fresh Install
- Harness GitOps Agent with Existing Argo CD instance
Select No, and then select Start.
In Name, enter the name for the new Agent.
In Namespace, enter the namespace where you want to install the Harness GitOps Agent. Typically, this is the target namespace for your deployment.
- For this tutorial, let's use the
defaultnamespace to install the Agent and deploy applications.
- For this tutorial, let's use the
Select Continue. The Review YAML settings appear.
This is the manifest YAML for the Harness GitOps Agent. You will download this YAML file and run it in your Harness GitOps Agent cluster.
kubectl apply -f gitops-agent.yml -n defaultSelect Continue and verify the Agent is successfully installed and can connect to Harness.
Select Yes, and then select Start.
In Name, enter the name for the existing Agent CD Project.
In Namespace, enter the namespace where you want to install the Harness GitOps Agent. Typically, this is the target namespace for your deployment.
Select Next. The Review YAML settings appear.
This is the manifest YAML for the Harness GitOps Agent. You will download this YAML file and run it in your Harness GitOps Agent cluster.
kubectl apply -f gitops-agent.yml -n defaultOnce you have installed the Agent, Harness will start importing all the entities from the existing Argo CD Project.
Repositories
A Harness GitOps Repository is a repo containing the declarative description of a desired state. The declarative description can be in Kubernetes manifests, Helm Chart, Kustomize manifests, etc.
- Select Settings, and then select Repositories.
- Select New Repository.
- Choose Git.
- Enter a name in Repository.
- In GitOps Agent, choose the Agent that you installed in your cluster and select Apply.
- In Git Repository URL, paste
https://github.com/GITHUB_USERNAME/harnesscd-example-apps.gitand replace GITHUB_USERNAME with your GitHub username. - Select Continue, and then choose Specify Credentials For Repository.
- Choose HTTPS as the Connection Type.
- Select Anonymous (no credentials required) as the Authentication method.
- Select Save & Continue and wait for Harness to verify the connection.
- Finally, select Finish.
Clusters
A Harness GitOps Cluster is the target deployment cluster that is compared to the desire state. Clusters are synced with the source manifests you add as GitOps Repositories.
- Select Settings, and then select Clusters.
- Select New Cluster.
- In Name, enter a name for the cluster.
- In GitOps Agent, choose the Agent that you installed in your cluster and select Apply.
- Select Continue and use Use the credentials of a specific Harness GitOps Agent.
- Select Save & Continue and wait for Harness to verify the connection.
- Finally, select Finish.
Applications
GitOps Applications are how you manage GitOps operations for a given desired state and its live instantiation.
A GitOps Application collects the Repository (what you want to deploy), Cluster (where you want to deploy), and Agent (how you want to deploy). You define these entities and then select them when you set up your Application.
- Select Applications.
Select New Application.
Enter the Application Name
guestbook.In the GitOps Agent, choose the Agent that you installed in your cluster and select Apply.
Select New Service, and then toggle to YAML for the YAML editor.
Select Edit YAML, paste the following YAML and select Save.
service:
name: gitopsguestbook
identifier: gitopsguestbook
serviceDefinition:
type: Kubernetes
spec: {}
gitOpsEnabled: trueSelect New Environment, and then toggle to YAML for the YAML editor.
Select Edit YAML, paste the following YAML and select Save.
environment:
name: gitopsenv
identifier: gitopsenv
description: ""
tags: {}
type: PreProduction
orgIdentifier: default
projectIdentifier: default_project
variables: []Select Continue, keep the Sync Policy settings as is, and then select Continue.
In Repository URL, choose the Repository you created earlier and select Apply.
Select master as the Target Revision, type
kustomize-guestbookin the Path, and press Enter.Select Continue to select the Cluster created in the above steps.
Enter the target Namespace for Harness GitOps to sync the application. Type
defaultand select Finish.
Finally, it's time to Synchronize the Apllication state. Select Sync, check the Application details, and then select Synchronize to initiate the deployment.
After a successful execution, you can check the deployment on your Kubernetes cluster using the following command:
kubectl get pods -n defaultTo access the Guestbook application deployed via the Harness pipeline, port forward the service and access it at http://localhost:8080:
kubectl port-forward svc/kustomize-guestbook-ui 8080:80
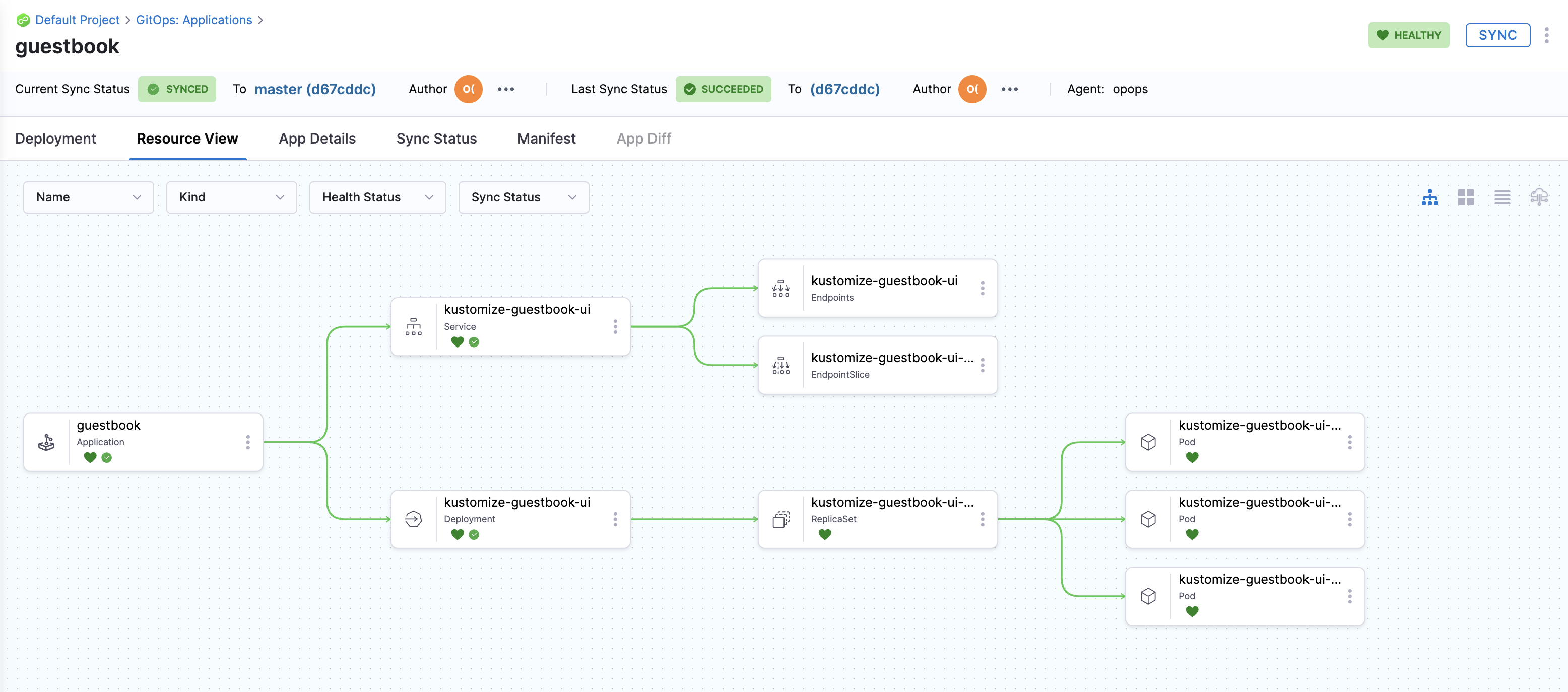
On successful Application sync, you'll see the below status tree under Resource View.
Congratulations!🎉
You've just learned how to use Harness GitOps to deploy an application using a Kustomize template.
What's Next?
- Keep learning about Harness GitOps. Create a GitOps ApplicationSet and PR Pipeline in Harness GitOps by following this guide.
- Visit the Harness Developer Hub for more tutorials and resources.