Cache Intelligence
Modern continuous integration systems execute pipelines inside ephemeral environments that are provisioned solely for pipeline execution and are not reused from prior pipeline runs. As builds often require downloading and installing many library and software dependencies, caching these dependencies for quick retrieval at runtime can save a significant amount of time.
There are several ways to configure caching in Harness CI, such as Cache Intelligence, Save and Restore Cache steps, and mounting volumes. Save and Restore Cache steps and mounted volumes require you to manage the cache. With Cache Intelligence, Harness automatically caches and restores common dependencies. Cache Intelligence also doesn't require you to bring your own storage, because the cache is stored in the Harness-hosted environment, Harness Cloud.
Supported build infrastructures
Currently, Cache Intelligence is only available for Linux and Windows platforms on Harness Cloud, the Harness-hosted build environment.
For other build infrastructures, you can use Save and Restore Cache steps, such as Save and Restore Cache from S3, to include caching in your CI pipelines.
Supported tools and paths
Cache Intelligence fully supports Bazel, Maven, Gradle, Yarn, Go, and Node build tools, if the dependencies are stored in the default location for that tool.
For other build tools or non-default cache locations, you can leverage Harness Cloud's cache storage by enabling Cache Intelligence and providing custom cache paths.
Cache storage
Harness Cloud allows up to 2GB of cache storage per account. All pipelines in the account use the same cache storage, and each build tool has a unique cache key that is used to restore the appropriate cache data at runtime.
The cache retention window is 15 days, which resets whenever the cache is updated.
Enable Cache Intelligence
- Visual
- YAML
Currently, the Cache Intelligence Visual Editor fields are behind the feature flag CI_CACHE_INTELLIGENCE. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
- Edit the pipeline, and select the Build stage where you want to enable Cache Intelligence.
- Select the Overview tab for the stage.
- Select Enable Cache Intelligence.
- If you're using an unsupported build tool, a non-default cache location, or a Windows platform, then you must add custom cache paths. For a list of supported tools, go to Supported tools and paths.
- Optionally, you can add a custom cache key.
To enable Cache Intelligence in the YAML editor, add the following lines to the stage.spec:
caching:
enabled: true
For example:
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
caching:
enabled: true
cloneCodebase: true
If you're using an unsupported build tool, a non-default cache location, or a Windows platform, you must add custom cache paths. For a list of supported tools, go to Supported tools and paths.
Optionally, you can add a custom cache key.
Customize cache paths
Cache Intelligence stores the data to be cached in the /harness directory by default. You can use paths to specify a list of locations to be cached. This is useful if:
- Cache Intelligence is not supported for your build tool.
- You have customized cache locations, such as with
yarn config set cache-folder. - You're using a Windows platform.
- Visual
- YAML
Currently, the Cache Intelligence Visual Editor fields are behind the feature flag CI_CACHE_INTELLIGENCE. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
Edit the pipeline, and select the Build stage where you want to enable Cache Intelligence.
Select the Overview tab for the stage.
Make sure Enable Cache Intelligence is selected.
Add Paths to cache.
Note that on Windows platforms, you might need to specify the cache path from
C:, such asC:\harness\node_modules.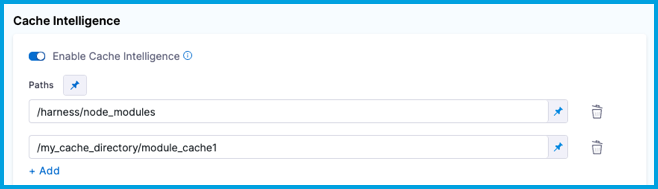
If a cache path is outside the
/harnessdirectory, you must also specify this in Shared Paths.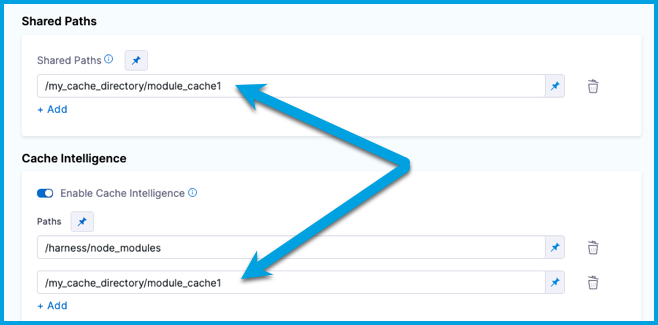
In the YAML editor, add a list of paths to cache under stage.spec.caching, for example:
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
caching:
enabled: true
paths:
- /harness/node_modules ## On a Windows platform, the path would be 'C:\harness\node_modules'.
cloneCodebase: true
...
If a cache path is outside the /harness directory, you must also specify this as a shared path. In the YAML editor, add a list of sharedPaths under stage.spec, for example:
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
caching:
enabled: true
paths:
- /harness/node_modules
- /my_cache_directory/module_cache1
cloneCodebase: true
...
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
sharedPaths:
- /my_cache_directory/module_cache1
Customize cache keys
Harness generates a cache key from a hash of the build lock file (such as pom.xml, build.gradle, or package.json) that Harness detects. If Harness detects multiple tools or multiple lock files, Harness combines the hashes to create the cache key.
- Visual
- YAML
Currently, the Cache Intelligence Visual Editor fields are behind the feature flag CI_CACHE_INTELLIGENCE. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
Edit the pipeline, and select the Build stage where you want to enable Cache Intelligence.
Select the Overview tab for the stage.
Make sure Enable Cache Intelligence is selected.
Enter the custom key value in Key. You can use fixed values, runtime inputs, and expressions for the key value.
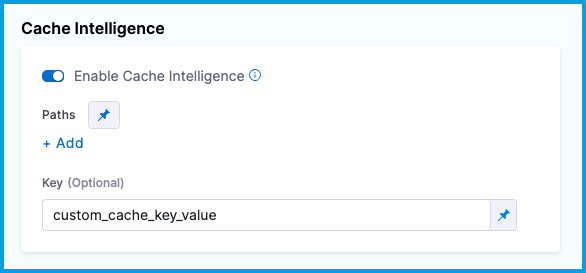
To customize the cache key in the YAML editor, add key: CUSTOM_KEY_VALUE under stage.spec.caching. You can use fixed values, runtime inputs, and expressions for the key value.
The following YAML example uses <+input>, which prompts the user to supply a cache key value at runtime.
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
caching:
enabled: true
key: <+input>
cloneCodebase: true
...
Cache Intelligence API
You can use the Cache Intelligence API to get information about the cache or delete the cache.
To invoke these APIs, you must have an API key with core_account_edit permissions. For information about API keys, go to Manage API keys.
Get cache metadata
Get metadata about the cache, such as the size and path.
curl --location --request GET 'https://app.harness.io/gateway/ci/cache/info?accountIdentifier=$HARNESS_ACCOUNT_ID' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer $AUTH_TOKEN'
Delete cache
Delete the cache. You can include an optional path parameter to delete a specific sub-directory in the cache.
curl --location --request DELETE 'https://app.harness.io/gateway/ci/cache/info?accountIdentifier=$HARNESS_ACCOUNT_ID&path=/path/to/deleted/directory' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer $AUTH_TOKEN'